Bees Vanish, and Scientists Race for Reasons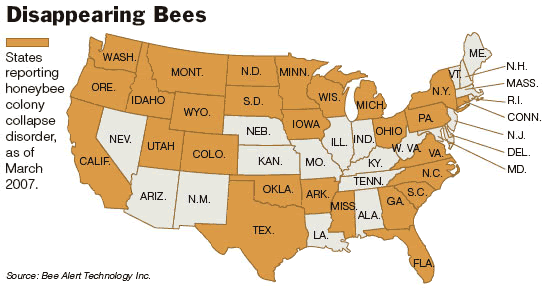
Honeybee colonies around the nation are collapsing:
The volume of theories to explain the collapse of honeybee populations “is totally mind-boggling,” said Diana Cox-Foster, an entomologist at Penn State.
More than a quarter of the country’s 2.4 million bee colonies have been lost — tens of billions of bees, according to an estimate from the Apiary Inspectors of America, a national group that tracks beekeeping. So far, no one can say what is causing the bees to become disoriented and fail to return to their hives.
As with any great mystery, a number of theories have been posed, and many seem to researchers to be more science fiction than science. People have blamed genetically modified crops, cellular phone towers and high-voltage transmission lines for the disappearances. Or was it a secret plot by Russia or Osama bin Laden to bring down American agriculture? Or, as some blogs have asserted, the rapture of the bees, in which God recalled them to heaven? Researchers have heard it all.
The volume of theories “is totally mind-boggling,” said Diana Cox-Foster, an entomologist at Pennsylvania State University. With Jeffrey S. Pettis, an entomologist from the United States Department of Agriculture, Dr. Cox-Foster is leading a team of researchers who are trying to find answers to explain “colony collapse disorder,” the name given for the disappearing bee syndrome.
“Clearly there is an urgency to solve this,” Dr. Cox-Foster said. “We are trying to move as quickly as we can.”
Dr. Cox-Foster and fellow scientists who are here at a two-day meeting to discuss early findings and future plans with government officials have been focusing on the most likely suspects: a virus, a fungus or a pesticide.
About 60 researchers from North America sifted the possibilities at the meeting today. Some expressed concern about the speed at which adult bees are disappearing from their hives; some colonies have collapsed in as little as two days. Others noted that countries in Europe, as well as Guatemala and parts of Brazil, are also struggling for answers.
“There are losses around the world that may or not be linked,” Dr. Pettis said.
The investigation is now entering a critical phase. The researchers have collected samples in several states and have begun doing bee autopsies and genetic analysis. Cross-sections of a diseased bee thorax, left, and a healthy one.
Cross-sections of a diseased bee thorax, left, and a healthy one.
So far, known enemies of the bee world, like the varroa mite, on their own at least, do not appear to be responsible for the unusually high losses.
Genetic testing at Columbia University has revealed the presence of multiple micro-organisms in bees from hives or colonies that are in decline, suggesting that something is weakening their immune system. The researchers have found some fungi in the affected bees that are found in humans whose immune systems have been suppressed by the Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome or cancer.
“That is extremely unusual,” Dr. Cox-Foster said.
Meanwhile, samples were sent to an Agriculture Department laboratory in North Carolina this month to screen for 117 chemicals. Particular suspicion falls on a pesticide that France banned out of concern that it may have been decimating bee colonies. Concern has also mounted among public officials.
“There are so many of our crops that require pollinators,” said Representative Dennis Cardoza, a California Democrat whose district includes that state’s central agricultural valley, and who presided last month at a Congressional hearing on the bee issue. “We need an urgent call to arms to try to ascertain what is really going on here with the bees, and bring as much science as we possibly can to bear on the problem.”
So far, colony collapse disorder has been found in 27 states, according to Bee Alert Technology Inc., a company monitoring the problem. A recent survey of 13 states by the Apiary Inspectors of America showed that 26 percent of beekeepers had lost half of their bee colonies between September and March.
Honeybees are arguably the insects that are most important to the human food chain. They are the principal pollinators of hundreds of fruits, vegetables, flowers and nuts. The number of bee colonies has been declining since the 1940s, even as the crops that rely on them, such as California almonds, have grown. In October, at about the time that beekeepers were experiencing huge bee losses, a study by the National Academy of Sciences questioned whether American agriculture was relying too heavily on one type of pollinator, the honeybee.
Bee colonies have been under stress in recent years as more beekeepers have resorted to crisscrossing the country with 18-wheel trucks full of bees in search of pollination work. These bees may suffer from a diet that includes artificial supplements, concoctions akin to energy drinks and power bars. In several states, suburban sprawl has limited the bees’ natural forage areas.
So far, the researchers have discounted the possibility that poor diet alone could be responsible for the widespread losses. They have also set aside for now the possibility that the cause could be bees feeding from a commonly used genetically modified crop, Bt corn, because the symptoms typically associated with toxins, such as blood poisoning, are not showing up in the affected bees. But researchers emphasized today that feeding supplements produced from genetically modified crops, such as high-fructose corn syrup, need to be studied.
The scientists say that definitive answers for the colony collapses could be months away. But recent advances in biology and genetic sequencing are speeding the search.
Computers can decipher information from DNA and match pieces of genetic code with particular organisms. Luckily, a project to sequence some 11,000 genes of the honeybee was completed late last year at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, giving scientists a huge head start on identifying any unknown pathogens in the bee tissue.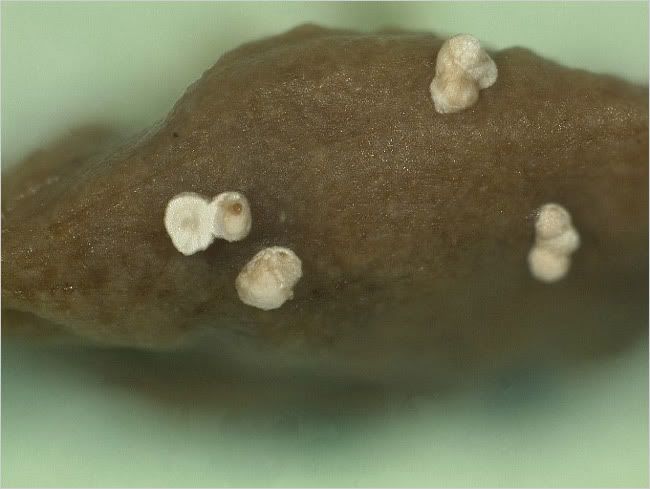 Globules in a bee’s gut may indicate lethal pathogens
Globules in a bee’s gut may indicate lethal pathogens
“Otherwise, we would be looking for the needle in the haystack,” Dr. Cox-Foster said.
Large bee losses are not unheard of. They have been reported at several points in the past century. But researchers think they are dealing with something new — or at least with something previously unidentified.
Cross-sections of a diseased bee thorax, left, and a healthy one.
“There could be a number of factors that are weakening the bees or speeding up things that shorten their lives,” said Dr. W. Steve Sheppard, a professor of entomology at Washington State University. “The answer may already be with us.”
Scientists first learned of the bee disappearances in November, when David Hackenberg, a Pennsylvania beekeeper, told Dr. Cox-Foster that more than 50 percent of his bee colonies had collapsed in Florida, where he had taken them for the winter.
Dr. Cox-Foster, a 20-year veteran of studying bees, soon teamed with Dennis vanEngelsdorp, the Pennsylvania apiary inspector, to look into the losses.
In December, she approached W. Ian Lipkin, director of the Greene Infectious Disease Laboratory at Columbia University, about doing genetic sequencing of tissue from bees in the colonies that experienced losses. The laboratory uses a recently developed technique for reading and amplifying short sequences of DNA that has revolutionized the science. Dr. Lipkin, who typically works on human diseases, agreed to do the analysis, despite not knowing who would ultimately pay for it. His laboratory is known for its work in finding the West Nile disease in the United States.
Dr. Cox-Foster ultimately sent samples of bee tissue to researchers at Columbia, to the Agriculture Department laboratory in Maryland, and to Gene Robinson, an entomologist at the University of Illinois. Fortuitously, she had frozen bee samples from healthy colonies dating to 2004 to use for comparison.
After receiving the first bee samples from Dr. Cox-Foster on March 6, Dr. Lipkin’s team amplified the genetic material and started sequencing to separate virus, fungus and parasite DNA from bee DNA.
“This is like C.S.I. for agriculture,” Dr. Lipkin said. “It is painstaking, gumshoe detective work.”
Dr. Lipkin sent his first set of results to Dr. Cox-Foster, showing that several unknown micro-organisms were present in the bees from collapsing colonies. Meanwhile, Mr. vanEngelsdorp and researchers at the Agriculture Department lab here began an autopsy of bees from collapsing colonies in California, Florida, Georgia and Pennsylvania to search for any known bee pathogens.
At the University of Illinois, using knowledge gained from the sequencing of the bee genome, Dr. Robinson’s team will try to find which genes in the collapsing colonies are particularly active, perhaps indicating stress from exposure to a toxin or pathogen.
The national research team also quietly began a parallel study in January, financed in part by the National Honey Board, to further determine if something pathogenic could be causing colonies to collapse.
Mr. Hackenberg, the beekeeper, agreed to take his empty bee boxes and other equipment to Food Technology Service, a company in Mulberry, Fla., that uses gamma rays to kill bacteria on medical equipment and some fruits. In early results, the irradiated bee boxes seem to have shown a return to health for colonies repopulated with Australian bees.
“This supports the idea that there is a pathogen there,” Dr. Cox-Foster said. “It would be hard to explain the irradiation getting rid of a chemical.”
Still, some environmental substances remain suspicious.
Chris Mullin, a Pennsylvania State University professor and insect toxicologist, recently sent a set of samples to a federal laboratory in Raleigh, N.C., that will screen for 117 chemicals. Of greatest interest are the “systemic” chemicals that are able to pass through a plant’s circulatory system and move to the new leaves or the flowers, where they would come in contact with bees.
One such group of compounds is called neonicotinoids, commonly used pesticides that are used to treat corn and other seeds against pests. One of the neonicotinoids, imidacloprid, is commonly used in Europe and the United States to treat seeds, to protect residential foundations against termites and to help keep golf courses and home lawns green.
In the late 1990s, French beekeepers reported large losses of their bees and complained about the use of imidacloprid, sold under the brand name Gaucho. The chemical, while not killing the bees outright, was causing them to be disoriented and stay away from their hives, leading them to die of exposure to the cold, French researchers later found. The beekeepers labeled the syndrome “mad bee disease.”
The French government banned the pesticide in 1999 for use on sunflowers, and later for corn, despite protests by the German chemical giant Bayer, which has said its internal research showed the pesticide was not toxic to bees. Subsequent studies by independent French researchers have disagreed with Bayer. Alison Chalmers, an eco-toxicologist for Bayer CropScience, said at the meeting today that bee colonies had not recovered in France as beekeepers had expected. “These chemicals are not being used anymore,” she said of imidacloprid, “so they certainly were not the only cause.”
Among the pesticides being tested in the American bee investigation, the neonicotinoids group “is the number-one suspect,” Dr. Mullin said. He hoped results of the toxicology screening will be ready within a month.
skip to main |
skip to sidebar
Reference materials' site for The Constant American.
Latest From CNN
Must Reading
- Life Inc.: How The World Became a Corporation and How To Take It Back by Douglas Rushkoff
- The Dark Side: The Inside Story of How The War on Terror Turned into a War on American Ideals by Jane Mayer
- Torture Team: Rumsfeld's Memo and the Betrayal of American Values by Philippe Sands
- Class 11: Inside the CIA's First Post-9/11 Spy Class by T.J. Waters
- The Terror Dream: Fear and Fantasy in Post-9/11 American by Susan Faludi
- The Shock Doctrine: The Rise of Disaster Capitalism by Naomi Klein
- A Pretext for War: 9/11, Iraq, and the Abuse of America's Intelligence Agencies by James Bamford
- The Italian Letter: How the Bush Administration Used a Fake Letter to Build the Case for War in Iraq by Peter Eisner
- Blue Covenant: The Global Water Crisis and the Coming Battle for the Right to Water by Maude Barlow
- The One Percent Doctrine by Ron Suskind
- Nemesis: The Last Days of the American Republic (American Empire Project) by Chalmers Johnson
- Free Lunch: How the Weathiest Americans Enrich Themselves at Government Expense (and Stick You with the Bill) by David Cay Johnston
- You Have No Rights: Stories of America in an Age of Repression by Matthew Rothschild
- What We Say Goes: Conversations on U.S. Power in a Changing World by Noam Chomsky, David Barsamian
- Blink: The Power of Thinking Without Thinking by Malcolm Gladwell
- Blackwater: The Rise of the World's Most Powerful Mercenary Army by Jeremy Scahill
- Whose Freedom?: The Battle Over America's Most Important Idea by George Lakoff
- Blue Gold: The Fight to Stop the Corporate Theft of the World's Water by Maude Barlow and Tony Clarke
- Don't Think of an Elephant: Know Your Values and Frame the Debate--The Essential Guide for Progressives by George Lakoff
- Perfectly Legal: The Covert Campaign to Rig Our Tax System to Benefit the Super Rich--and Cheat Everybody Else by David Cay Johnston
- The Tipping Point: How Little Things Can Make a Big Difference by Malcolm Gladwell
- Unequal Protection: The Rise of Corporate Dominance and the Theft of Human Rights by Thom Hartmann
- Secrecy & Privilege | Neck Deep
- The Unwanted Gaze: The Destruction of Privacy in America by Jeffrey Rosen
- The October Surprise Mystery
- The Seven Sisters: The great oil companies & the world they shaped
- People's History of the United States by Howard Zinn
- The Student As Nigger by Jerry Farber
Bright Ideas
********************************
Energy Generating Dance Floor
******************************** Stop Junk Mail
********************************
C O N T R I B U T O R S
- Maeven
Blogs on Military Intelligence
Iraq & Afghanistan
Reference Sites
Reference Files
Document File
- [alternative address]
- Analysis-How to train death squads and quash revolutions from San Salvador to Iraq
- Foreclosed: State of the Dream 2008
- Memorandum: Construction Workers Camp at the New Embassy Compound, Baghdad
- OLC Torture Memo-May 10, 2005 (20 pages)
- OLC Torture Memo-May 10, 2005 (46 pages)
- OLC Torture Memo-May 2002
- OLC Torture Memo-May 30, 2005 (40 pages)
- Questions Raised about the Conduct of the State Department Inspector General
- The First Report of the Congressional Oversight Panel for Economic Stabilization
- U.S. Army memo: Collecting Information on U.S. Persons
- U.S. Army: Civilian Inmate Prison Camps on Army Installations
- U.S. CounterInsurgency Manual
- U.S. CounterInsurgency Manual-1994 Version
- U.S. Special Forces CounterInsurgency Manuel - WikiLeaks
Climate Change
What"s Up In The Universe?
Let's Go To The Movies!
[+/-] expand/collapse
Life Inc., The Movie
James Burke's After The Warming
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 1 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 2 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 3 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 4 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 5 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 6 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 7 of 7 "Distorted Morality," a lecture by Noam Chomsky: Noam Chomsky on BookTV, 4/17/07, Part 1: Noam Chomsky on BookTV, 4/17/07, Part 2: Noam Chomsky at MIT, "The Militarization of Science and Space": Noam Chomsky's "Manufacturing Consent": 9/11 Truth: Unusual Evacuations
* * * * * * *
Torturing Democracy* * * * * * *
Peace, Propaganda and the Promised Land The Revolution Will Not Be Televised - The Smartest Guys in the RoomEnron
Posted Jun 08, 2006Full Version
Iraq's Missing Billions War Made Easy The Big Buy - The Rise and Fall of Tom Delay Iraq: The Hidden Story Iraq For Sale - a Robert Greenwald film The Secret Government - PBS, Bill Moyers The History of Oil - Robert Newman The Power of Nightmares "Confessions of an Economic Hitman," an interview with the author, John Perkins: "America: Freedom to Fascism," a film by Aaron Russo: Greg Palast, "How Bush Stole The 2000 Election," Part 1 of 2: Sir, No Sir! Greg Palast, "How Bush Stole The 2000 Election," Part 2 of 2: Noam Chomsky vs Alan DershowitzIsrael And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 1 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 2 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 3 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 4 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 5 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 6 of 7 Noam Chomsky vs Alan Dershowitz
Israel And Palestine After Disengagement: "Where Do We Go From Here?"
Harvard University 11/29/05
Part 7 of 7 "Distorted Morality," a lecture by Noam Chomsky: Noam Chomsky on BookTV, 4/17/07, Part 1: Noam Chomsky on BookTV, 4/17/07, Part 2: Noam Chomsky at MIT, "The Militarization of Science and Space": Noam Chomsky's "Manufacturing Consent": 9/11 Truth: Unusual Evacuations
ExperiLabels [+/-]
- 10th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals (1)
- 110th Congress (1)
- 1949 Geneva Conventions (4)
- 1949 Geneva Conventions-Fourth (1)
- 1949 Geneva Conventions-Third (1)
- 501 (c) (4) (1)
- 60 Minutes (1)
- 7th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals (1)
- 9/11/01 (34)
- 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals (2)
- Aaron Mate (1)
- Abd al-Rahim al-Nahsiri (1)
- Abdul-Mahdi (1)
- abortion (10)
- Abu Dhabi (1)
- Abu Ghraib (19)
- Abu Zubaydah (2)
- ACLU (3)
- activism (3)
- acts of misdirection? (3)
- Admiral Michael Mullen (1)
- advisory Board (1)
- Afghan civilians (1)
- Afghanistan (10)
- Ahmed Chalabi (1)
- Al Gore (4)
- Al Kamen (1)
- Al Qaeda (16)
- Al Sharpton (4)
- al-Hashemi (2)
- al-Mahdi (1)
- al-Maliki (11)
- al-Sistani (1)
- Alabama (3)
- Alan Greenspan (1)
- Alan Mollohan (1)
- Alan Simpson (1)
- Alaska (10)
- Alberto Gonzales (26)
- Alberto Mora (1)
- Alfa Group (1)
- Alphonse D'Amato (1)
- alternative media (1)
- amendment 2073 (1)
- American culture (49)
- American Petroleum Institute (1)
- Amy Goodman (7)
- An Inconvenient Truth (1)
- Analysis Corp (1)
- Anbar (3)
- Andrea Mitchell (1)
- Andrew Card (5)
- animals (15)
- Another Bush cock-up (4)
- Anthony Cordesman (1)
- Anthony Kennedy (1)
- Anthony Zinni (1)
- anthrax (6)
- antiquities (1)
- Antonia Juhasz (2)
- AQI (1)
- Arent Fox Kintner Plotkin and Kahn (1)
- Ari Fleischer (1)
- Arizona (3)
- Arkansas (1)
- Arlen Specter (14)
- arms sales (3)
- Armstrong Williams (3)
- Arnold Schwarzenegger (1)
- art (3)
- asbestos (2)
- Atlanta (1)
- audio (2)
- AUMF 2002 (1)
- Australia (1)
- Bab al-Sheik (1)
- Baghdad (1)
- Bagram (1)
- bailout (4)
- Bakhtawar Zardari (1)
- Bangladesh (1)
- Baqouba (1)
- Barack Obama (43)
- Barbara Bush (5)
- Barry Jackson (1)
- Basra (2)
- BCCI (2)
- Bearing Point (1)
- bees (2)
- Ben Bernanke (1)
- Ben Nelson (2)
- Benazir Bhutto (7)
- benchmarks (3)
- Benita Fitzgerald Mosley (2)
- Benjamin Netanyahu (1)
- Big Agra (7)
- Big Business (2)
- Big Oil (12)
- Big Pharma (1)
- BigAgra (1)
- Bilawal Bhutto (2)
- Bill Clinton (19)
- Bill Clinton was no friend to liberals (1)
- Bill Gates (1)
- Bill Keller (1)
- Bill Kristol (2)
- Bill Maher (1)
- Bill Moyers (2)
- Bill Richardson (3)
- Bill Sammon (2)
- birds (1)
- Blackstone (2)
- Blackwater (11)
- blogging (4)
- Bob Baer (2)
- Bob Corker (1)
- Bob Graham (1)
- Bob Perry (1)
- Bob Shrum (1)
- Bobby Jindal (2)
- Bolivia (1)
- books (30)
- boys will be boys (1)
- BP (4)
- BP America (1)
- BP PLC (1)
- Brad Delong (1)
- Bradley Schlozman (1)
- Brazil (1)
- Bremer's 100 Orders (2)
- Brent Scowcroft (3)
- Brewster Jennings (1)
- Brian Schweitzer (1)
- Brigadier General Janis Karpinski (3)
- Bruce Bartlett (1)
- Bruce Fein (1)
- Bruce McMahan (2)
- Bud Cummins (1)
- Bulgaria (1)
- Bureau of Diplomatic Security (1)
- Burma (3)
- Bush (89)
- Bush 1 administration (2)
- Bush administration (98)
- Bush family (2)
- Bush veto (4)
- Bush-speak (1)
- Bush's legacy (5)
- Bush's surge (38)
- CAFTA (1)
- California (20)
- Cambodia (1)
- Camp Bucca (2)
- Camp Cropper (1)
- campaign contributors (1)
- Canada (1)
- cancer (1)
- candidates' positions (1)
- capitalism (3)
- Carl Levin (4)
- Carl Lindner (1)
- Carlyle Group (3)
- Carol Lam (1)
- Caroline Cheeks Kilpatrick (1)
- CBO (1)
- CBS (3)
- celebrity gossip (2)
- censorship (3)
- Centers for Disease Control (1)
- Chad (1)
- Chalmers Johnson (1)
- Charles Duelfer (2)
- Charles Grassley (6)
- Charles Koch (2)
- Charlie Rangel (1)
- charts (1)
- Chechnya (1)
- chemical industry (1)
- Chevron (3)
- ChevronTexaco (1)
- Chicago (2)
- children (1)
- China (12)
- Chip Reid (1)
- Chris Dodd (4)
- Chris Hedges (1)
- Chris Matthews (10)
- Chris Van Hollen (2)
- Christian Coalition (1)
- Christine Todd Whitman (3)
- Christopher Hitchens (1)
- Chuck Schumer (9)
- CIA (36)
- CIA leak investigation (4)
- CIA tapes (1)
- Cindy Sheehan (3)
- Citibank (1)
- civil liberties (4)
- civil rights (5)
- Claire McCaskill (1)
- Clarence Page (2)
- Clarence Thomas (1)
- Cleveland (1)
- climate change (8)
- Clinton administration (2)
- cluster bombs (3)
- CNN (1)
- coal (2)
- Coalition Provisional Authority (4)
- Cofer Black (2)
- Cold War (2)
- Colin Powell (5)
- Colleen Rowley (3)
- Colombia (1)
- Colonel Thomas M. Pappas (3)
- Colorado (3)
- Condoleeza Rice (5)
- Congo (1)
- Congressional Record (1)
- Connecticut (1)
- Conoco (1)
- ConocoPhillips (1)
- Conservatives (5)
- conspicuous consumption (12)
- Contempt of Congress (2)
- contractors (17)
- corn (5)
- corporate welfare (1)
- corruption (27)
- Council for National Policy (4)
- Council on Foreign Relations (1)
- CPA (9)
- Craig Crawford (2)
- Craig Fuller (1)
- Craig Thomas (1)
- crumbling infrastructure (1)
- Cuba (11)
- culture (22)
- Curveball (1)
- Cynthia Tucker (1)
- Cyril Wecht (1)
- Czech Republic (1)
- D and E/D and X/Partial Birth Abortion (2)
- D.C. voting rights (1)
- Dan Abrams (1)
- Dan Bartlett (2)
- Dan Burton (1)
- Dan Metcalfe (1)
- Dan Rather (1)
- Daniel Ellsberg (2)
- Daniel Inouye (1)
- Darrell Issa (2)
- David Addington (1)
- David Albright (2)
- David Broder (1)
- David Brooks (1)
- David Frum (1)
- David Gergen (2)
- David Gregory (8)
- David Gribben (1)
- David Horgan (1)
- David Kay (1)
- David Koch (2)
- David M. McIntosh (1)
- David MacMichael (2)
- David Rivkin (1)
- David Shuster (1)
- David Vitter (6)
- death penalty (2)
- death toll (1)
- debates (5)
- Debra Wong Yang (1)
- Defense Appropriations Subcommittee (1)
- Defense Authoriation Act of 2006 (1)
- Defense Policy Board (1)
- Deforest Soaries (3)
- Democracy Now (11)
- Democratic Party (4)
- Democratic Presidential debates (2)
- Democrats (9)
- Democrats suck too (39)
- Denmark (2)
- Dennis Kucinich (3)
- Department of Homeland Security (3)
- deregulation (17)
- derivatives (1)
- Det Norske Oljeselskap (1)
- detainees (2)
- Detroit (2)
- Diane Beaver (1)
- Dianne Feinstein (7)
- Dick Cheney (37)
- Dick Cheney's energy task force (4)
- Dick Durbin (4)
- Dick Lugar (2)
- dirty tricks (17)
- dissent (1)
- Diyala (1)
- DLC politics (1)
- DNO (2)
- documents (1)
- DoD (1)
- dogs (2)
- DOJ (5)
- domestic spying (1)
- Don Evans (4)
- Don Imus (6)
- Don Siegelman (1)
- Donald Rumsfeld (12)
- Douglas Brinkley (1)
- Douglas Feith (4)
- Dr. Justin Frank (1)
- draft (2)
- Drew Westen (1)
- drought (2)
- drug bill (1)
- drugs-illicit (4)
- drugs-pharmaceutical (1)
- Duncan Hunter (1)
- E.J. Dionne (1)
- earmarks (4)
- Ebay (1)
- economics (23)
- economy (81)
- Ecuador (1)
- Ed Markey (1)
- Ed Rogers (1)
- education (5)
- Egypt (2)
- Ehud Olmert (1)
- El Salvador (2)
- election 1980 (1)
- election 1992 (1)
- election 2000 (8)
- election 2002 (1)
- election 2008 (45)
- election reform (4)
- elections 2002 (2)
- elections 2004 (1)
- elections 2006 (4)
- elections 2008 (76)
- elections 2012 (1)
- electionws 2004 (1)
- Elian Gonzalez (1)
- Elijah Cummings (1)
- Elizabeth Dole (1)
- Ellen Tauscher (1)
- Elliot Abrams (1)
- email (4)
- ENDGAME (1)
- endorsements (3)
- energy (13)
- energy nuclear (2)
- energy nuclear (1)
- energy policy (6)
- entertainment (7)
- environment (59)
- environmental (1)
- EPA (3)
- Eric Edelman (1)
- Eric Holder (1)
- Eric Prince (2)
- Estonia (1)
- ethanol (1)
- ethics (2)
- Eugene Robinson (2)
- European Union (1)
- executive order 12334 (1)
- executive order 12472 (1)
- executive order 12656 (1)
- executive order 12958 (1)
- executive order 13228 (1)
- executive order 13233 (2)
- executive order 13303 (1)
- executive order 13315 (1)
- executive order 13350 (1)
- executive orders (8)
- Executive Privilege (4)
- Exxon (1)
- ExxonMobil (5)
- Fairness Doctrine (1)
- faith-based organizations (2)
- Fallujah (2)
- Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (1)
- Farm Bill (5)
- Faye Williams (1)
- FBI (16)
- FCC (2)
- FDA (6)
- FDIC (1)
- FEC (1)
- Federal Reserve (4)
- Federalist Society (1)
- FEMA (1)
- filibuster (1)
- financial disclosure (1)
- first amendment (11)
- FISA bill (13)
- fish (3)
- flat tax (1)
- FOIA (1)
- food (46)
- For the children (2)
- For the common good (2)
- Foreign Intelligence cronyism (1)
- fourth amendment (1)
- Fox News (1)
- France (2)
- Frances Townsend (2)
- Frank Murkowski (1)
- Frank Rich (1)
- Frank Riggs (1)
- Fred Fielding (2)
- Fred Koch (1)
- Fred Thompson (15)
- free speech (3)
- free trade (1)
- freedom and democracy in Iraq (6)
- Freedom of Information Act of 2007 (1)
- Freedom to dissent...NOT (1)
- Freedom's Watch (2)
- Frontline (1)
- FUBAR (7)
- Futile Care Law (1)
- Gail Norton (2)
- GAO (7)
- gay rights (3)
- Gaza (2)
- Gazprom (1)
- gender inequality (4)
- Genel Enerji (1)
- General David Petraeus (6)
- General Electric (1)
- General Eric Shenseki (1)
- General Michael Hayden (6)
- General Tommy Franks (1)
- George H.W. Bush (10)
- George Lakoff (1)
- George P. Bush (1)
- George Tenet (15)
- George Voinovich (1)
- Georgia (7)
- Georgia Maryland (1)
- Georgia Pacific Corp. (1)
- Georgia Thompson (1)
- Germany (4)
- Getting To Know Your Adversary (1)
- Glass-Steagall Act of 1933 (1)
- Glenn Greenwald (1)
- global warming (20)
- globalization (2)
- GMO (2)
- Gonzales vs. Carhart (1)
- GOP (12)
- Gordon Brown (2)
- Governor Jim Doyle (1)
- Great Britain (22)
- Greg Thielmann (1)
- Grover Norquist (3)
- Guantanamo (20)
- Guatemala (1)
- Gulf of Mexico (2)
- Gulf War 1 (3)
- guns (2)
- H.R. 1255 (1)
- H.R. 1591 (1)
- H.R. 2206 (1)
- H.R. 3222 (1)
- H.R. 4156 (1)
- H.R. 4241 (1)
- Hague Regulations of 1907 (3)
- Haiti (1)
- Haley Barbour (1)
- Halliburton (6)
- Hamid Karzai (1)
- Hardball (16)
- Harold Ford Jr. (1)
- Harold Ickes (1)
- Harold Simmons (1)
- Harriet Miers (4)
- Harry Reid (9)
- Hatch Act (1)
- Hawaii (1)
- health (65)
- health care reform (1)
- health insurance (6)
- hearings (1)
- hedge fund managers (2)
- hedge funds (2)
- Helms-Burton Act (1)
- Henry Kissinger (1)
- Henry Paulson (3)
- Henry Waxman (8)
- Hezbollah (1)
- Hillary Clinton (62)
- holidays (2)
- homeland security (2)
- Homeland Security appropriations bill (1)
- House Appropriations Committee (3)
- House Committee on Intelligence (3)
- House Committee on Oversight and Government Reform (6)
- House Foreign Affairs Committee (1)
- House Judiciary Committee (5)
- House Natural Resources Committee (1)
- House Republicans (6)
- housing (1)
- Howard Fineman (3)
- Howard Wolfson (1)
- HR 1955 (1)
- HSPD 20 (2)
- Huffington Post (1)
- Hugo Chavez (2)
- human rights (13)
- Hungary (1)
- Hurricane Katrina (2)
- Hypocrisy 101 (4)
- Idaho (1)
- Ideas Whose Time Has Come? (1)
- illegal immigration (7)
- Illinois (3)
- IMF (4)
- impeachment (12)
- implosions (10)
- In our names (19)
- India (1)
- Indiana (4)
- Indonesia (1)
- insurgency (1)
- intelligence (9)
- Internet (7)
- interviews (19)
- Invocon (1)
- Iowa (3)
- IPO (1)
- Iran (27)
- Iran-Contra (1)
- Iran-Iraq war (1)
- Iraq (42)
- Iraq czar (1)
- Iraq elections (2)
- Iraq Health Ministry (1)
- Iraq occupation (2)
- Iraq Petroleum Company (1)
- Iraq reconstruction (5)
- Iraq Study Group (1)
- Iraq Survey Group (2)
- Iraqi army (1)
- Iraqi civilians (13)
- Iraqi Islamic Party (1)
- Ireland (1)
- Ishaqi (1)
- Islam (1)
- Israel (18)
- Issam Al-Chalabi (1)
- Italy (1)
- Iyad Allawi (1)
- Jack Abramoff (1)
- Jack Reed (2)
- James Baker (2)
- James Carville (3)
- James Comey (6)
- James Dobson (1)
- James Inholfe (1)
- James K. Haveman (1)
- James Schlesinger (1)
- James Sensenbrenner (1)
- James Woolsey (3)
- James Yousef Yee (1)
- Jan Schakowsky (1)
- Jane Dalton (1)
- Jane Harman (3)
- Japan (2)
- Jay Dardenne (1)
- Jay Leno (1)
- Jay Rockefeller (6)
- Jean Shaheen (4)
- Jean-Baptiste Aristide (1)
- Jean-Bertrand Aristide (1)
- Jeff Sessions (3)
- Jeffrey Toobin (1)
- Jennifer Fitzgerald (1)
- Jeremy Scahill (3)
- Jerrold Nadler (2)
- Jerry Lewis (1)
- Jesse Helms (1)
- Jesse Jackson (1)
- Jill Abramson (1)
- Jim Bunning (1)
- Jim DeMint (2)
- Jim Donelon (1)
- Jim Gilmore (1)
- Jim Hightower (2)
- Jim Marcinkowski (1)
- Jim McCrery (1)
- Jim McGovern (1)
- Jim Miklaszewski (1)
- Jim Moran (1)
- Jim O'Beirne (2)
- Jim Rogers (3)
- Jim VandeHei (1)
- Jim Webb (2)
- Jimmy Breslin (1)
- Jimmy Carter (1)
- Jo Ann Emerson (1)
- Joan Baez (1)
- Joe Allbaugh (1)
- Joe Biden (4)
- Joe Conason (3)
- Joe DiGenova (2)
- Joe Klein (1)
- Joe Lieberman (5)
- Joe Scarborough (1)
- Joe Wilson (9)
- John Ashcroft (7)
- John B. Taylor (1)
- John Barrasso (1)
- John Boehner (3)
- John Bolton (1)
- John Conyers (5)
- John Cornyn (1)
- John D. Bates (1)
- John Danforth (1)
- John Dean (2)
- John Dingell (2)
- John Edwards (9)
- John Gilmore (2)
- John Harris (2)
- John Harwood (2)
- John Kerry (3)
- John King (1)
- John McCain (11)
- John Mellencamp (1)
- John Murtha (3)
- John Nichols (2)
- John Roberts (4)
- John Sununu (3)
- John Warner (4)
- John Yoo (1)
- John Zogby (1)
- Joint Chiefs of Staff (2)
- Jon Corzine (1)
- Jonathan Alter (2)
- Jonathan Cohn (1)
- Jonathan Turley (1)
- Jordan (4)
- Jose Padilla (1)
- Joseph Stiglitz (1)
- Josh Bolten (2)
- Judith Miller (2)
- Judith Nathan Giuliani (1)
- K Street (2)
- Kamil Mubdir Gailani (1)
- Karbala (1)
- Karen Hughes (1)
- Karl Rove (25)
- Kate O'Beirne (2)
- Kazakhstan (1)
- Keith Olbermann (6)
- Ken Blackwell (1)
- Ken Mehlman (1)
- Ken Pollack (1)
- Ken Salazar (1)
- Ken Starr (1)
- Ken Wainstein (1)
- Kennedy family (1)
- Kenneth Blackwell (1)
- Kentucky (1)
- Ketchum (1)
- Khalid Sheik Mohammed (1)
- King Abdullah (1)
- Kit Bond (2)
- Kitty Kelley (1)
- knuckle-dragging Americans (1)
- Koch brothers (2)
- Koch Industries (1)
- KRG (1)
- Kristin Breitweiser (1)
- Kurdistan (3)
- Kurdistan Regional Government (2)
- Kurds (7)
- Kyle Sampson (1)
- L-1 Identity Solutions (1)
- Lamar Alexander (2)
- Lancet study (9)
- Lanny Griffith (1)
- Larry Craig (2)
- Larry Ellison (1)
- Larry Johnson (2)
- Larry Lindsey (1)
- Larry Summers (1)
- Larry Wilkerson (1)
- Las Vegas (3)
- Latvia (1)
- Laura Bush (1)
- Laurie David (1)
- Lawrence Korb (1)
- Leandro Aragoncillo (1)
- Lebanon (3)
- Lee Hamilton (1)
- legislation (30)
- Leon Panetta (1)
- Liberals (2)
- Libya (4)
- Lieutenant General Ricardo S. Sanchez (1)
- Lindsay Graham (6)
- Lisa Murkowski (1)
- lobbyists (6)
- Lockerbie (3)
- Lois Romano (1)
- London (1)
- long war (1)
- Loretta Sanchez (1)
- Lou Dubose (1)
- Louisiana (7)
- Lt. Colonel Steven Jordan (2)
- Lt. General Douglas Lute (2)
- Lt. General Martin Dempsey (1)
- Lt. General Ricardo Sanchez (1)
- Lukoil (1)
- Lynndie England (1)
- Madrid bombings (1)
- Mahdi Army (1)
- Mahmoom Khaghani (1)
- Maine (3)
- mainstream media (8)
- Major General Antonio Taguba (1)
- Major General Benjamin R. Mixon (1)
- Major General Geoffrey Miller (11)
- maps (1)
- Margaret Carlson (1)
- Marion Spike Bowman (2)
- Mark Corallo (1)
- Mark McKinnon (1)
- Mark Mix (1)
- Mark Penn (2)
- Mark Pryor (1)
- martial law (1)
- Mary Beth Buchanan (3)
- Mary Cheney (1)
- Mary Landrieu (1)
- Mary Matalin (2)
- Maryland (2)
- Massachusetts (2)
- Matt Brooks (1)
- Matt Cooper (1)
- Matthew Mead (1)
- Maury Wills (1)
- Max Baucus (1)
- media (15)
- Medicaid (1)
- medical ethics (1)
- Meet the Press (4)
- Meghan O'Sullivan (1)
- Mel Sembler (1)
- meltdown (16)
- men (1)
- mental health (11)
- mental illness (6)
- Mexico (4)
- Michael Allan Leach (1)
- Michael Bloomberg (1)
- Michael Chertoff (6)
- Michael Eric Dyson (1)
- Michael Garcia (1)
- Michael Ledeen (1)
- Michael Moore (4)
- Michael Mukasey (13)
- Michael O'Hanlon (2)
- Michael Pollan (7)
- Michael R. Gordon (2)
- Michael Scheuer (2)
- Michael Steele (1)
- Michael Turk (1)
- Michelle Obama (1)
- Michigan (2)
- Mickey Herskowitz (1)
- Middle East (15)
- Mike Barnicle (1)
- Mike Huckabee (9)
- Mike McConnell (3)
- Mike Mullen (1)
- military budget (5)
- Military Commissions Act of 2006 (1)
- military equipment (15)
- Military Industrial Complex (4)
- military tribunals (1)
- Milwaukee (1)
- Minnesota (2)
- Mississippi (2)
- Missouri (1)
- Mitch McConnell (4)
- Mitt Romney (9)
- Molly Ivins (2)
- moments in history (1)
- Monica Goodling (1)
- Monica Lewinsky (1)
- Montana (3)
- Most Ethical Congress (1)
- MoveOn.org (2)
- movies (2)
- MSNBC (3)
- multinational corporations (2)
- Murray Waas (2)
- N. Korea (4)
- NAFTA (3)
- Najaf (1)
- Nancy Pelosi (16)
- Naomi Klein (10)
- Naomi Wolf (1)
- narcissistic personality disorder (1)
- Nat Parry (1)
- National Defense Authorization Act for 2008 (4)
- National Guard (2)
- National Republican Congressional Committee (1)
- National Security (1)
- National Security Archive (2)
- National Security Decision Directive 188 (1)
- Neil Bush (2)
- Nelson Cohen (3)
- Neoconservatives (4)
- Netherlands (1)
- Nevada (1)
- New Afghanistan (3)
- New Hampshire (8)
- New Iraq (51)
- New Jersey (1)
- New Orleans (1)
- New World Order (9)
- New York (7)
- New York Times (5)
- New Yorker (1)
- Newsweek (8)
- Newt Gingrich (2)
- NIE (4)
- NIH (1)
- Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals (2)
- No Child Left Behind (1)
- No WMD (2)
- Noam Chomsky (1)
- Norm Coleman (1)
- North Carolina (3)
- Now That Obama's President - What's Left To Do? (1)
- NRC (1)
- NRCC (1)
- NSA (6)
- NSL (2)
- NSPD 51 (2)
- nuclear (12)
- Obama administration (10)
- obituaries (2)
- oceans (4)
- offshoring (1)
- Ohio (3)
- oil (14)
- oil and gas (20)
- oil law (21)
- Oklahoma (1)
- Oliver North (1)
- Olympia Snowe (1)
- OPEC (3)
- Operation Clean Break (1)
- Operation Rescue (1)
- Oprah Winfrey (1)
- Order 37 (2)
- Order 39 (3)
- Order 40 (1)
- Oregon (1)
- organic farming (1)
- organized labor (7)
- Orrin Hatch (1)
- Osama Bin Laden (9)
- outsourcing (1)
- owls (1)
- PACS (1)
- Pakistan (15)
- Pakistan's People's Party (2)
- Palestinians (2)
- Pan Am 103 (2)
- Paris Hilton (2)
- parliamentary procedure (1)
- passportgate (2)
- Pat Buchanan (4)
- Pat Leahy (2)
- Pat Roberts (4)
- Pat Tillman (2)
- Patrick Lang (1)
- Patrick Leahy (10)
- Patrick McHenry (1)
- Patriot Act (12)
- Patty Murray (1)
- Paul Allen (1)
- Paul Bremer (9)
- Paul Craig Roberts (1)
- Paul Eaton (1)
- Paul Krugman (8)
- Paul O'Neill (1)
- Paul Rieckhoff (2)
- Paul Wellstone (1)
- Paul Weyrich (1)
- Paul Wolfowitz (5)
- PDVSA (1)
- Peak oil (2)
- Pennsylvania (4)
- Pentagon (22)
- people (1)
- Pervez Musharraf (10)
- Pete Domenici (1)
- Peter King (1)
- Petoil (1)
- Petrel Resources (1)
- Phil Gingrey (1)
- Phil Giraldi (1)
- Phil Griffin (1)
- Philip Atkinson (1)
- Philip Zelikow (1)
- Phillipines (2)
- photos (66)
- Phyllis Schlafly (1)
- PKK (1)
- Plan B (1)
- PNAC (1)
- Poland (1)
- police brutality (2)
- political fundraising (1)
- political operatives (1)
- polls (4)
- population control (1)
- Porter Goss (2)
- poverty in America (3)
- Presidential candidates (8)
- Presidential Directives (1)
- Presidential pardons (1)
- Presidential Records Act of 1978 (6)
- press releases (1)
- prewar intelligence (1)
- Prince Bandar bin Sultan (2)
- prisons (6)
- privacy (15)
- Privacy Act of 1974 (1)
- private contractors (1)
- private equity (2)
- privatization (20)
- Profiles (11)
- Project Checkmate (1)
- propaganda (4)
- Protect America Act (2)
- PSA (1)
- psychologists (1)
- Psychology Today (1)
- PTSD (1)
- public relations (1)
- Puerto Rico (2)
- Pulitizer prizes (1)
- Putin (3)
- QinetiQ (1)
- Quds (1)
- race card (7)
- Rachel Maddow (3)
- racism (4)
- Rahm Emanuel (1)
- Ramadi (1)
- Ramzi Yousef (1)
- Rand Corporation (2)
- Ray McGovern (6)
- Reagan administration (1)
- real estate (2)
- Reasons not to vote for Republicans (22)
- Reasons we need campaign finance reform (7)
- recess appointment (1)
- red flags (1)
- reference file (1)
- reference papers (1)
- refugees (3)
- religion (3)
- rendition (2)
- reports (1)
- Republican Party (3)
- Republicans (15)
- Richard Armitage (1)
- Richard Baker (1)
- Richard Clarke (1)
- Richard E. Stickler (1)
- Richard Mellon Scaife (2)
- Richard Nixon (2)
- Richard Perle (6)
- Richard Viguerie (1)
- Richard Wolffe (1)
- Rick Santorum (1)
- right-wing organizations (2)
- RNC (7)
- Robert Dreyfuss (1)
- Robert F. Kennedy Jr. (2)
- Robert Fisk (1)
- Robert Gates (9)
- Robert Johnson (1)
- Robert Kuttner (1)
- Robert Mueller (10)
- Robert Novak (3)
- Robert Parry (6)
- Robert Reich (1)
- Rodney Alexander (1)
- Roger Simon (2)
- Roger Stone (2)
- Romania (1)
- Ron Brownstein (2)
- Ron Paul (3)
- Ron Reagan (1)
- Ron Suskind (1)
- Ron Wyden (1)
- Ronald Reagan (3)
- Roslynn Mauskopf (1)
- Royal Dutch Shell (3)
- Royal Dutch/Shell Group of Cos. (1)
- Rudy Giuliani (5)
- Rudy Guiliani (1)
- rule of law (8)
- Rush Holt (1)
- Russ Feingold (2)
- Russell Feingold (1)
- Russell Simmons (1)
- Russia (4)
- Rwanda (1)
- Ryan Crocker (3)
- S. 1927 (4)
- S. 1932 (1)
- S. 2340 (1)
- S. Carolina (4)
- S. Dakota (1)
- S. Korea (1)
- Sabrina D. Harman (1)
- Saddam Hussein (3)
- Sadr City (1)
- SAIC (1)
- Sam Bodman (1)
- Sam Brownback (2)
- Samarra (2)
- San Francisco (4)
- sanctions (1)
- Sandra Day O'Connor (2)
- Sara Taylor (4)
- Sarah Palin (7)
- Sarkozy (1)
- Saudi Arabia (17)
- Savings and Loan crisis (3)
- science (2)
- Scooter Libby (8)
- Scott Ritter (2)
- SEC (1)
- secrecy (12)
- secret government (2)
- secret holds (1)
- secret prisons (4)
- Secret Service (3)
- secular democracy (1)
- Senate Appropriations subcommittee (2)
- Senate Armed Services Committee (3)
- Senate Energy and Commerce Committee (1)
- Senate Ethics Committee (1)
- Senate Finance Committee (2)
- Senate Intelligence Committee (6)
- Senate Judiciary Committee (22)
- Senate Republicans (1)
- senior issues (2)
- Separation of church and state (8)
- Sergeant Michael J. Smith (1)
- Sergeant Santos A. Cardona (1)
- sex (1)
- sex crimes (1)
- Seymour Hersh (7)
- Sheldon Adelson (2)
- Shell Oil (6)
- Sheryl Crow (1)
- Shiite militias (1)
- shrines (2)
- Sibel Edmonds (1)
- Sibiyha Prince (1)
- Sidney Blumenthal (2)
- SIGIR (1)
- signing statements (1)
- Slovakia (1)
- slow food (2)
- socialism (1)
- SOFA (1)
- Spain (2)
- Special Inspector General for Iraq Reconstruction (1)
- special ops (1)
- Specialist Charles Graner (1)
- speeches (2)
- Stephen Cambone (1)
- Stephen Hadley (8)
- Steve Capus (2)
- Steve Fraser (1)
- Steve McMahon (2)
- Steve Scalise (1)
- Steven Biskupic (1)
- Stuart Bowen (1)
- summer reading list (1)
- Sunni (2)
- sunshine laws (1)
- superdelegates (2)
- supplemental appropriations bill (9)
- Susan Collins (2)
- Susan Page (1)
- Susan Ralston (1)
- Swift Boat veterans (1)
- Swift Boat Veterans for Truth (1)
- Syria (13)
- T. Boone Pickens (1)
- Taguba report (2)
- Talabani (2)
- Taliban (2)
- TALON (1)
- TANG (1)
- taxes (1)
- Ted Kennedy (1)
- Ted Olson (1)
- Ted Stevens (2)
- Telecommunications Act (1)
- Telecoms (2)
- Tennessee (1)
- terrorism (12)
- Terrorist Surveillance Program (6)
- Terry McAuliffe (1)
- Terry O'Donnell (1)
- Texas (11)
- Thailand (1)
- The Fellowship (1)
- think tanks (3)
- Thom Hartmann (1)
- Thomas B. Edsall (1)
- Thomas Blanton (1)
- Thomas Edsall (1)
- Thomas J. Collamore (1)
- Thomas M. Tamm (1)
- Tim Geithner (7)
- Tim Griffin (1)
- Tim LaHaye (1)
- Tim Russert (2)
- Tim Ryan (1)
- Timothy P. Berry (1)
- Todd Graves (1)
- Todd Palin (3)
- Tom Allen (1)
- Tom Andrews (1)
- Tom Brokaw (1)
- Tom Coburn (1)
- Tom Coburt (1)
- Tom Daschle (1)
- Tom Davis (4)
- Tom DeLay (2)
- Tom Harkin (1)
- Tom Lantos (1)
- Tom Maertens (1)
- Tom Oliphant (1)
- Tom Tancredo (1)
- Tom Vilsack (1)
- Tommy Chong (1)
- Tony Blair (7)
- Tony Blankley (2)
- Tony Snow (2)
- tort reform (1)
- torture (51)
- Total (1)
- transcripts (47)
- trauma (2)
- Trent Lott (1)
- trial attorneys (1)
- TSA (1)
- Turkey (4)
- Tyler Drumheller (2)
- Tyumen Oil (1)
- U.S. Air Force (1)
- U.S. Army (2)
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (1)
- U.S. Army's Law of Land Warfare (1)
- U.S. Attorney Bill (1)
- U.S. Attorney General (8)
- U.S. Attorneys (23)
- U.S. bases (2)
- U.S. budget (1)
- U.S. Congress (16)
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (5)
- U.S. Department of Homeland Security (13)
- U.S. Department of Justice (3)
- U.S. Department of the Interior (1)
- U.S. Department of Transportation (1)
- U.S. District Court (1)
- U.S. dollar (4)
- U.S. Empire (1)
- U.S. foreign policy (18)
- U.S. House (10)
- U.S. military (62)
- U.S. Senate (13)
- U.S. State Department (6)
- U.S. Supreme Court (3)
- U.S. trade policies (5)
- U.S. Treasury Department (2)
- U.S.A. (1)
- U.S.S.C. (6)
- UAE (2)
- Ukraine (1)
- UN (7)
- UN Human Rights Commission (1)
- UN resolution 1483 (1)
- UN resolution 1546 (1)
- UN Security Council Resolution 687 (1)
- UNCC (1)
- UNICEF (1)
- unitary executive (2)
- Utah (2)
- Vaclav Klaus (1)
- Valerie Jarrett (1)
- Valerie Plame (12)
- Venezuela (2)
- Vermont (1)
- veterans affairs (1)
- VFW (1)
- Vicente Fox (1)
- video (26)
- video links (1)
- videos (21)
- Vince Cannistraro (1)
- Violence in America (1)
- Virginia (6)
- Vivian Stringer (1)
- voter caging (1)
- voter fraud (5)
- voter ID (3)
- Wal-Mart (1)
- Walter Reed Army Medical Center (1)
- war (2)
- war crimes (16)
- war czar (3)
- war in Afghanistan (24)
- war in Iran (19)
- war in Iraq (300)
- war in Vietnam (2)
- war on terror (51)
- war reparations (1)
- warrantless wiretaps (23)
- Warren Buffett (2)
- Washington (1)
- water (12)
- Watergate (1)
- Wayne LaPierre (1)
- wealth disparity (1)
- weapons (2)
- Wendy Cortez (1)
- Western Oilsands (1)
- Westinghouse (1)
- What The Hell Are They Thinking? (1)
- What's the matter with (4)
- Where are the Democrats? (3)
- whistleblowers (2)
- White House Office of Administration (1)
- White House Press Briefing (4)
- Who Broke America? (1)
- Why they hate us (11)
- William Arkin (1)
- William E. Colby (1)
- William J. Haynes (1)
- William Koch (1)
- William Kristol (2)
- William P. Weidner (1)
- William Pryor Jr. (1)
- Wisconsin (2)
- WMD (6)
- Wolf Blitzer (1)
- Wolfeboro (1)
- women (12)
- World Bank (3)
- worthless media (7)
- wounded veterans (2)
- WTO (1)
- Wyoming (1)
- Xe (2)
- Your tax dollars (2)
- YouTube (1)
- Zarqawi (2)
- Zogby (1)
- Zulfikar Ali Bhutto (1)
Labels
- 10th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals (1)
- 110th Congress (1)
- 1949 Geneva Conventions (4)
- 1949 Geneva Conventions-Fourth (1)
- 1949 Geneva Conventions-Third (1)
- 501 (c) (4) (1)
- 60 Minutes (1)
- 7th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals (1)
- 9/11/01 (34)
- 9th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals (2)
- Aaron Mate (1)
- Abd al-Rahim al-Nahsiri (1)
- Abdul-Mahdi (1)
- abortion (10)
- Abu Dhabi (1)
- Abu Ghraib (19)
- Abu Zubaydah (2)
- ACLU (3)
- activism (3)
- acts of misdirection? (3)
- Admiral Michael Mullen (1)
- advisory Board (1)
- Afghan civilians (1)
- Afghanistan (10)
- Ahmed Chalabi (1)
- Al Gore (4)
- Al Kamen (1)
- Al Qaeda (16)
- Al Sharpton (4)
- al-Hashemi (2)
- al-Mahdi (1)
- al-Maliki (11)
- al-Sistani (1)
- Alabama (3)
- Alan Greenspan (1)
- Alan Mollohan (1)
- Alan Simpson (1)
- Alaska (10)
- Alberto Gonzales (26)
- Alberto Mora (1)
- Alfa Group (1)
- Alphonse D'Amato (1)
- alternative media (1)
- amendment 2073 (1)
- American culture (49)
- American Petroleum Institute (1)
- Amy Goodman (7)
- An Inconvenient Truth (1)
- Analysis Corp (1)
- Anbar (3)
- Andrea Mitchell (1)
- Andrew Card (5)
- animals (15)
- Another Bush cock-up (4)
- Anthony Cordesman (1)
- Anthony Kennedy (1)
- Anthony Zinni (1)
- anthrax (6)
- antiquities (1)
- Antonia Juhasz (2)
- AQI (1)
- Arent Fox Kintner Plotkin and Kahn (1)
- Ari Fleischer (1)
- Arizona (3)
- Arkansas (1)
- Arlen Specter (14)
- arms sales (3)
- Armstrong Williams (3)
- Arnold Schwarzenegger (1)
- art (3)
- asbestos (2)
- Atlanta (1)
- audio (2)
- AUMF 2002 (1)
- Australia (1)
- Bab al-Sheik (1)
- Baghdad (1)
- Bagram (1)
- bailout (4)
- Bakhtawar Zardari (1)
- Bangladesh (1)
- Baqouba (1)
- Barack Obama (43)
- Barbara Bush (5)
- Barry Jackson (1)
- Basra (2)
- BCCI (2)
- Bearing Point (1)
- bees (2)
- Ben Bernanke (1)
- Ben Nelson (2)
- Benazir Bhutto (7)
- benchmarks (3)
- Benita Fitzgerald Mosley (2)
- Benjamin Netanyahu (1)
- Big Agra (7)
- Big Business (2)
- Big Oil (12)
- Big Pharma (1)
- BigAgra (1)
- Bilawal Bhutto (2)
- Bill Clinton (19)
- Bill Clinton was no friend to liberals (1)
- Bill Gates (1)
- Bill Keller (1)
- Bill Kristol (2)
- Bill Maher (1)
- Bill Moyers (2)
- Bill Richardson (3)
- Bill Sammon (2)
- birds (1)
- Blackstone (2)
- Blackwater (11)
- blogging (4)
- Bob Baer (2)
- Bob Corker (1)
- Bob Graham (1)
- Bob Perry (1)
- Bob Shrum (1)
- Bobby Jindal (2)
- Bolivia (1)
- books (30)
- boys will be boys (1)
- BP (4)
- BP America (1)
- BP PLC (1)
- Brad Delong (1)
- Bradley Schlozman (1)
- Brazil (1)
- Bremer's 100 Orders (2)
- Brent Scowcroft (3)
- Brewster Jennings (1)
- Brian Schweitzer (1)
- Brigadier General Janis Karpinski (3)
- Bruce Bartlett (1)
- Bruce Fein (1)
- Bruce McMahan (2)
- Bud Cummins (1)
- Bulgaria (1)
- Bureau of Diplomatic Security (1)
- Burma (3)
- Bush (89)
- Bush 1 administration (2)
- Bush administration (98)
- Bush family (2)
- Bush veto (4)
- Bush-speak (1)
- Bush's legacy (5)
- Bush's surge (38)
- CAFTA (1)
- California (20)
- Cambodia (1)
- Camp Bucca (2)
- Camp Cropper (1)
- campaign contributors (1)
- Canada (1)
- cancer (1)
- candidates' positions (1)
- capitalism (3)
- Carl Levin (4)
- Carl Lindner (1)
- Carlyle Group (3)
- Carol Lam (1)
- Caroline Cheeks Kilpatrick (1)
- CBO (1)
- CBS (3)
- celebrity gossip (2)
- censorship (3)
- Centers for Disease Control (1)
- Chad (1)
- Chalmers Johnson (1)
- Charles Duelfer (2)
- Charles Grassley (6)
- Charles Koch (2)
- Charlie Rangel (1)
- charts (1)
- Chechnya (1)
- chemical industry (1)
- Chevron (3)
- ChevronTexaco (1)
- Chicago (2)
- children (1)
- China (12)
- Chip Reid (1)
- Chris Dodd (4)
- Chris Hedges (1)
- Chris Matthews (10)
- Chris Van Hollen (2)
- Christian Coalition (1)
- Christine Todd Whitman (3)
- Christopher Hitchens (1)
- Chuck Schumer (9)
- CIA (36)
- CIA leak investigation (4)
- CIA tapes (1)
- Cindy Sheehan (3)
- Citibank (1)
- civil liberties (4)
- civil rights (5)
- Claire McCaskill (1)
- Clarence Page (2)
- Clarence Thomas (1)
- Cleveland (1)
- climate change (8)
- Clinton administration (2)
- cluster bombs (3)
- CNN (1)
- coal (2)
- Coalition Provisional Authority (4)
- Cofer Black (2)
- Cold War (2)
- Colin Powell (5)
- Colleen Rowley (3)
- Colombia (1)
- Colonel Thomas M. Pappas (3)
- Colorado (3)
- Condoleeza Rice (5)
- Congo (1)
- Congressional Record (1)
- Connecticut (1)
- Conoco (1)
- ConocoPhillips (1)
- Conservatives (5)
- conspicuous consumption (12)
- Contempt of Congress (2)
- contractors (17)
- corn (5)
- corporate welfare (1)
- corruption (27)
- Council for National Policy (4)
- Council on Foreign Relations (1)
- CPA (9)
- Craig Crawford (2)
- Craig Fuller (1)
- Craig Thomas (1)
- crumbling infrastructure (1)
- Cuba (11)
- culture (22)
- Curveball (1)
- Cynthia Tucker (1)
- Cyril Wecht (1)
- Czech Republic (1)
- D and E/D and X/Partial Birth Abortion (2)
- D.C. voting rights (1)
- Dan Abrams (1)
- Dan Bartlett (2)
- Dan Burton (1)
- Dan Metcalfe (1)
- Dan Rather (1)
- Daniel Ellsberg (2)
- Daniel Inouye (1)
- Darrell Issa (2)
- David Addington (1)
- David Albright (2)
- David Broder (1)
- David Brooks (1)
- David Frum (1)
- David Gergen (2)
- David Gregory (8)
- David Gribben (1)
- David Horgan (1)
- David Kay (1)
- David Koch (2)
- David M. McIntosh (1)
- David MacMichael (2)
- David Rivkin (1)
- David Shuster (1)
- David Vitter (6)
- death penalty (2)
- death toll (1)
- debates (5)
- Debra Wong Yang (1)
- Defense Appropriations Subcommittee (1)
- Defense Authoriation Act of 2006 (1)
- Defense Policy Board (1)
- Deforest Soaries (3)
- Democracy Now (11)
- Democratic Party (4)
- Democratic Presidential debates (2)
- Democrats (9)
- Democrats suck too (39)
- Denmark (2)
- Dennis Kucinich (3)
- Department of Homeland Security (3)
- deregulation (17)
- derivatives (1)
- Det Norske Oljeselskap (1)
- detainees (2)
- Detroit (2)
- Diane Beaver (1)
- Dianne Feinstein (7)
- Dick Cheney (37)
- Dick Cheney's energy task force (4)
- Dick Durbin (4)
- Dick Lugar (2)
- dirty tricks (17)
- dissent (1)
- Diyala (1)
- DLC politics (1)
- DNO (2)
- documents (1)
- DoD (1)
- dogs (2)
- DOJ (5)
- domestic spying (1)
- Don Evans (4)
- Don Imus (6)
- Don Siegelman (1)
- Donald Rumsfeld (12)
- Douglas Brinkley (1)
- Douglas Feith (4)
- Dr. Justin Frank (1)
- draft (2)
- Drew Westen (1)
- drought (2)
- drug bill (1)
- drugs-illicit (4)
- drugs-pharmaceutical (1)
- Duncan Hunter (1)
- E.J. Dionne (1)
- earmarks (4)
- Ebay (1)
- economics (23)
- economy (81)
- Ecuador (1)
- Ed Markey (1)
- Ed Rogers (1)
- education (5)
- Egypt (2)
- Ehud Olmert (1)
- El Salvador (2)
- election 1980 (1)
- election 1992 (1)
- election 2000 (8)
- election 2002 (1)
- election 2008 (45)
- election reform (4)
- elections 2002 (2)
- elections 2004 (1)
- elections 2006 (4)
- elections 2008 (76)
- elections 2012 (1)
- electionws 2004 (1)
- Elian Gonzalez (1)
- Elijah Cummings (1)
- Elizabeth Dole (1)
- Ellen Tauscher (1)
- Elliot Abrams (1)
- email (4)
- ENDGAME (1)
- endorsements (3)
- energy (13)
- energy nuclear (2)
- energy nuclear (1)
- energy policy (6)
- entertainment (7)
- environment (59)
- environmental (1)
- EPA (3)
- Eric Edelman (1)
- Eric Holder (1)
- Eric Prince (2)
- Estonia (1)
- ethanol (1)
- ethics (2)
- Eugene Robinson (2)
- European Union (1)
- executive order 12334 (1)
- executive order 12472 (1)
- executive order 12656 (1)
- executive order 12958 (1)
- executive order 13228 (1)
- executive order 13233 (2)
- executive order 13303 (1)
- executive order 13315 (1)
- executive order 13350 (1)
- executive orders (8)
- Executive Privilege (4)
- Exxon (1)
- ExxonMobil (5)
- Fairness Doctrine (1)
- faith-based organizations (2)
- Fallujah (2)
- Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (1)
- Farm Bill (5)
- Faye Williams (1)
- FBI (16)
- FCC (2)
- FDA (6)
- FDIC (1)
- FEC (1)
- Federal Reserve (4)
- Federalist Society (1)
- FEMA (1)
- filibuster (1)
- financial disclosure (1)
- first amendment (11)
- FISA bill (13)
- fish (3)
- flat tax (1)
- FOIA (1)
- food (46)
- For the children (2)
- For the common good (2)
- Foreign Intelligence cronyism (1)
- fourth amendment (1)
- Fox News (1)
- France (2)
- Frances Townsend (2)
- Frank Murkowski (1)
- Frank Rich (1)
- Frank Riggs (1)
- Fred Fielding (2)
- Fred Koch (1)
- Fred Thompson (15)
- free speech (3)
- free trade (1)
- freedom and democracy in Iraq (6)
- Freedom of Information Act of 2007 (1)
- Freedom to dissent...NOT (1)
- Freedom's Watch (2)
- Frontline (1)
- FUBAR (7)
- Futile Care Law (1)
- Gail Norton (2)
- GAO (7)
- gay rights (3)
- Gaza (2)
- Gazprom (1)
- gender inequality (4)
- Genel Enerji (1)
- General David Petraeus (6)
- General Electric (1)
- General Eric Shenseki (1)
- General Michael Hayden (6)
- General Tommy Franks (1)
- George H.W. Bush (10)
- George Lakoff (1)
- George P. Bush (1)
- George Tenet (15)
- George Voinovich (1)
- Georgia (7)
- Georgia Maryland (1)
- Georgia Pacific Corp. (1)
- Georgia Thompson (1)
- Germany (4)
- Getting To Know Your Adversary (1)
- Glass-Steagall Act of 1933 (1)
- Glenn Greenwald (1)
- global warming (20)
- globalization (2)
- GMO (2)
- Gonzales vs. Carhart (1)
- GOP (12)
- Gordon Brown (2)
- Governor Jim Doyle (1)
- Great Britain (22)
- Greg Thielmann (1)
- Grover Norquist (3)
- Guantanamo (20)
- Guatemala (1)
- Gulf of Mexico (2)
- Gulf War 1 (3)
- guns (2)
- H.R. 1255 (1)
- H.R. 1591 (1)
- H.R. 2206 (1)
- H.R. 3222 (1)
- H.R. 4156 (1)
- H.R. 4241 (1)
- Hague Regulations of 1907 (3)
- Haiti (1)
- Haley Barbour (1)
- Halliburton (6)
- Hamid Karzai (1)
- Hardball (16)
- Harold Ford Jr. (1)
- Harold Ickes (1)
- Harold Simmons (1)
- Harriet Miers (4)
- Harry Reid (9)
- Hatch Act (1)
- Hawaii (1)
- health (65)
- health care reform (1)
- health insurance (6)
- hearings (1)
- hedge fund managers (2)
- hedge funds (2)
- Helms-Burton Act (1)
- Henry Kissinger (1)
- Henry Paulson (3)
- Henry Waxman (8)
- Hezbollah (1)
- Hillary Clinton (62)
- holidays (2)
- homeland security (2)
- Homeland Security appropriations bill (1)
- House Appropriations Committee (3)
- House Committee on Intelligence (3)
- House Committee on Oversight and Government Reform (6)
- House Foreign Affairs Committee (1)
- House Judiciary Committee (5)
- House Natural Resources Committee (1)
- House Republicans (6)
- housing (1)
- Howard Fineman (3)
- Howard Wolfson (1)
- HR 1955 (1)
- HSPD 20 (2)
- Huffington Post (1)
- Hugo Chavez (2)
- human rights (13)
- Hungary (1)
- Hurricane Katrina (2)
- Hypocrisy 101 (4)
- Idaho (1)
- Ideas Whose Time Has Come? (1)
- illegal immigration (7)
- Illinois (3)
- IMF (4)
- impeachment (12)
- implosions (10)
- In our names (19)
- India (1)
- Indiana (4)
- Indonesia (1)
- insurgency (1)
- intelligence (9)
- Internet (7)
- interviews (19)
- Invocon (1)
- Iowa (3)
- IPO (1)
- Iran (27)
- Iran-Contra (1)
- Iran-Iraq war (1)
- Iraq (42)
- Iraq czar (1)
- Iraq elections (2)
- Iraq Health Ministry (1)
- Iraq occupation (2)
- Iraq Petroleum Company (1)
- Iraq reconstruction (5)
- Iraq Study Group (1)
- Iraq Survey Group (2)
- Iraqi army (1)
- Iraqi civilians (13)
- Iraqi Islamic Party (1)
- Ireland (1)
- Ishaqi (1)
- Islam (1)
- Israel (18)
- Issam Al-Chalabi (1)
- Italy (1)
- Iyad Allawi (1)
- Jack Abramoff (1)
- Jack Reed (2)
- James Baker (2)
- James Carville (3)
- James Comey (6)
- James Dobson (1)
- James Inholfe (1)
- James K. Haveman (1)
- James Schlesinger (1)
- James Sensenbrenner (1)
- James Woolsey (3)
- James Yousef Yee (1)
- Jan Schakowsky (1)
- Jane Dalton (1)
- Jane Harman (3)
- Japan (2)
- Jay Dardenne (1)
- Jay Leno (1)
- Jay Rockefeller (6)
- Jean Shaheen (4)
- Jean-Baptiste Aristide (1)
- Jean-Bertrand Aristide (1)
- Jeff Sessions (3)
- Jeffrey Toobin (1)
- Jennifer Fitzgerald (1)
- Jeremy Scahill (3)
- Jerrold Nadler (2)
- Jerry Lewis (1)
- Jesse Helms (1)
- Jesse Jackson (1)
- Jill Abramson (1)
- Jim Bunning (1)
- Jim DeMint (2)
- Jim Donelon (1)
- Jim Gilmore (1)
- Jim Hightower (2)
- Jim Marcinkowski (1)
- Jim McCrery (1)
- Jim McGovern (1)
- Jim Miklaszewski (1)
- Jim Moran (1)
- Jim O'Beirne (2)
- Jim Rogers (3)
- Jim VandeHei (1)
- Jim Webb (2)
- Jimmy Breslin (1)
- Jimmy Carter (1)
- Jo Ann Emerson (1)
- Joan Baez (1)
- Joe Allbaugh (1)
- Joe Biden (4)
- Joe Conason (3)
- Joe DiGenova (2)
- Joe Klein (1)
- Joe Lieberman (5)
- Joe Scarborough (1)
- Joe Wilson (9)
- John Ashcroft (7)
- John B. Taylor (1)
- John Barrasso (1)
- John Boehner (3)
- John Bolton (1)
- John Conyers (5)
- John Cornyn (1)
- John D. Bates (1)
- John Danforth (1)
- John Dean (2)
- John Dingell (2)
- John Edwards (9)
- John Gilmore (2)
- John Harris (2)
- John Harwood (2)
- John Kerry (3)
- John King (1)
- John McCain (11)
- John Mellencamp (1)
- John Murtha (3)
- John Nichols (2)
- John Roberts (4)
- John Sununu (3)
- John Warner (4)
- John Yoo (1)
- John Zogby (1)
- Joint Chiefs of Staff (2)
- Jon Corzine (1)
- Jonathan Alter (2)
- Jonathan Cohn (1)
- Jonathan Turley (1)
- Jordan (4)
- Jose Padilla (1)
- Joseph Stiglitz (1)
- Josh Bolten (2)
- Judith Miller (2)
- Judith Nathan Giuliani (1)
- K Street (2)
- Kamil Mubdir Gailani (1)
- Karbala (1)
- Karen Hughes (1)
- Karl Rove (25)
- Kate O'Beirne (2)
- Kazakhstan (1)
- Keith Olbermann (6)
- Ken Blackwell (1)
- Ken Mehlman (1)
- Ken Pollack (1)
- Ken Salazar (1)
- Ken Starr (1)
- Ken Wainstein (1)
- Kennedy family (1)
- Kenneth Blackwell (1)
- Kentucky (1)
- Ketchum (1)
- Khalid Sheik Mohammed (1)
- King Abdullah (1)
- Kit Bond (2)
- Kitty Kelley (1)
- knuckle-dragging Americans (1)
- Koch brothers (2)
- Koch Industries (1)
- KRG (1)
- Kristin Breitweiser (1)
- Kurdistan (3)
- Kurdistan Regional Government (2)
- Kurds (7)
- Kyle Sampson (1)
- L-1 Identity Solutions (1)
- Lamar Alexander (2)
- Lancet study (9)
- Lanny Griffith (1)
- Larry Craig (2)
- Larry Ellison (1)
- Larry Johnson (2)
- Larry Lindsey (1)
- Larry Summers (1)
- Larry Wilkerson (1)
- Las Vegas (3)
- Latvia (1)
- Laura Bush (1)
- Laurie David (1)
- Lawrence Korb (1)
- Leandro Aragoncillo (1)
- Lebanon (3)
- Lee Hamilton (1)
- legislation (30)
- Leon Panetta (1)
- Liberals (2)
- Libya (4)
- Lieutenant General Ricardo S. Sanchez (1)
- Lindsay Graham (6)
- Lisa Murkowski (1)
- lobbyists (6)
- Lockerbie (3)
- Lois Romano (1)
- London (1)
- long war (1)
- Loretta Sanchez (1)
- Lou Dubose (1)
- Louisiana (7)
- Lt. Colonel Steven Jordan (2)
- Lt. General Douglas Lute (2)
- Lt. General Martin Dempsey (1)
- Lt. General Ricardo Sanchez (1)
- Lukoil (1)
- Lynndie England (1)
- Madrid bombings (1)
- Mahdi Army (1)
- Mahmoom Khaghani (1)
- Maine (3)
- mainstream media (8)
- Major General Antonio Taguba (1)
- Major General Benjamin R. Mixon (1)
- Major General Geoffrey Miller (11)
- maps (1)
- Margaret Carlson (1)
- Marion Spike Bowman (2)
- Mark Corallo (1)
- Mark McKinnon (1)
- Mark Mix (1)
- Mark Penn (2)
- Mark Pryor (1)
- martial law (1)
- Mary Beth Buchanan (3)
- Mary Cheney (1)
- Mary Landrieu (1)
- Mary Matalin (2)
- Maryland (2)
- Massachusetts (2)
- Matt Brooks (1)
- Matt Cooper (1)
- Matthew Mead (1)
- Maury Wills (1)
- Max Baucus (1)
- media (15)
- Medicaid (1)
- medical ethics (1)
- Meet the Press (4)
- Meghan O'Sullivan (1)
- Mel Sembler (1)
- meltdown (16)
- men (1)
- mental health (11)
- mental illness (6)
- Mexico (4)
- Michael Allan Leach (1)
- Michael Bloomberg (1)
- Michael Chertoff (6)
- Michael Eric Dyson (1)
- Michael Garcia (1)
- Michael Ledeen (1)
- Michael Moore (4)
- Michael Mukasey (13)
- Michael O'Hanlon (2)
- Michael Pollan (7)
- Michael R. Gordon (2)
- Michael Scheuer (2)
- Michael Steele (1)
- Michael Turk (1)
- Michelle Obama (1)
- Michigan (2)
- Mickey Herskowitz (1)
- Middle East (15)
- Mike Barnicle (1)
- Mike Huckabee (9)
- Mike McConnell (3)
- Mike Mullen (1)
- military budget (5)
- Military Commissions Act of 2006 (1)
- military equipment (15)
- Military Industrial Complex (4)
- military tribunals (1)
- Milwaukee (1)
- Minnesota (2)
- Mississippi (2)
- Missouri (1)
- Mitch McConnell (4)
- Mitt Romney (9)
- Molly Ivins (2)
- moments in history (1)
- Monica Goodling (1)
- Monica Lewinsky (1)
- Montana (3)
- Most Ethical Congress (1)
- MoveOn.org (2)
- movies (2)
- MSNBC (3)
- multinational corporations (2)
- Murray Waas (2)
- N. Korea (4)
- NAFTA (3)
- Najaf (1)
- Nancy Pelosi (16)
- Naomi Klein (10)
- Naomi Wolf (1)
- narcissistic personality disorder (1)
- Nat Parry (1)
- National Defense Authorization Act for 2008 (4)
- National Guard (2)
- National Republican Congressional Committee (1)
- National Security (1)
- National Security Archive (2)
- National Security Decision Directive 188 (1)
- Neil Bush (2)
- Nelson Cohen (3)
- Neoconservatives (4)
- Netherlands (1)
- Nevada (1)
- New Afghanistan (3)
- New Hampshire (8)
- New Iraq (51)
- New Jersey (1)
- New Orleans (1)
- New World Order (9)
- New York (7)
- New York Times (5)
- New Yorker (1)
- Newsweek (8)
- Newt Gingrich (2)
- NIE (4)
- NIH (1)
- Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals (2)
- No Child Left Behind (1)
- No WMD (2)
- Noam Chomsky (1)
- Norm Coleman (1)
- North Carolina (3)
- Now That Obama's President - What's Left To Do? (1)
- NRC (1)
- NRCC (1)
- NSA (6)
- NSL (2)
- NSPD 51 (2)
- nuclear (12)
- Obama administration (10)
- obituaries (2)
- oceans (4)
- offshoring (1)
- Ohio (3)
- oil (14)
- oil and gas (20)
- oil law (21)
- Oklahoma (1)
- Oliver North (1)
- Olympia Snowe (1)
- OPEC (3)
- Operation Clean Break (1)
- Operation Rescue (1)
- Oprah Winfrey (1)
- Order 37 (2)
- Order 39 (3)
- Order 40 (1)
- Oregon (1)
- organic farming (1)
- organized labor (7)
- Orrin Hatch (1)
- Osama Bin Laden (9)
- outsourcing (1)
- owls (1)
- PACS (1)
- Pakistan (15)
- Pakistan's People's Party (2)
- Palestinians (2)
- Pan Am 103 (2)
- Paris Hilton (2)
- parliamentary procedure (1)
- passportgate (2)
- Pat Buchanan (4)
- Pat Leahy (2)
- Pat Roberts (4)
- Pat Tillman (2)
- Patrick Lang (1)
- Patrick Leahy (10)
- Patrick McHenry (1)
- Patriot Act (12)
- Patty Murray (1)
- Paul Allen (1)
- Paul Bremer (9)
- Paul Craig Roberts (1)
- Paul Eaton (1)
- Paul Krugman (8)
- Paul O'Neill (1)
- Paul Rieckhoff (2)
- Paul Wellstone (1)
- Paul Weyrich (1)
- Paul Wolfowitz (5)
- PDVSA (1)
- Peak oil (2)
- Pennsylvania (4)
- Pentagon (22)
- people (1)
- Pervez Musharraf (10)
- Pete Domenici (1)
- Peter King (1)
- Petoil (1)
- Petrel Resources (1)
- Phil Gingrey (1)
- Phil Giraldi (1)
- Phil Griffin (1)
- Philip Atkinson (1)
- Philip Zelikow (1)
- Phillipines (2)
- photos (66)
- Phyllis Schlafly (1)
- PKK (1)
- Plan B (1)
- PNAC (1)
- Poland (1)
- police brutality (2)
- political fundraising (1)
- political operatives (1)
- polls (4)
- population control (1)
- Porter Goss (2)
- poverty in America (3)
- Presidential candidates (8)
- Presidential Directives (1)
- Presidential pardons (1)
- Presidential Records Act of 1978 (6)
- press releases (1)
- prewar intelligence (1)
- Prince Bandar bin Sultan (2)
- prisons (6)
- privacy (15)
- Privacy Act of 1974 (1)
- private contractors (1)
- private equity (2)
- privatization (20)
- Profiles (11)
- Project Checkmate (1)
- propaganda (4)
- Protect America Act (2)
- PSA (1)
- psychologists (1)
- Psychology Today (1)
- PTSD (1)
- public relations (1)
- Puerto Rico (2)
- Pulitizer prizes (1)
- Putin (3)
- QinetiQ (1)
- Quds (1)
- race card (7)
- Rachel Maddow (3)
- racism (4)
- Rahm Emanuel (1)
- Ramadi (1)
- Ramzi Yousef (1)
- Rand Corporation (2)
- Ray McGovern (6)
- Reagan administration (1)
- real estate (2)
- Reasons not to vote for Republicans (22)
- Reasons we need campaign finance reform (7)
- recess appointment (1)
- red flags (1)
- reference file (1)
- reference papers (1)
- refugees (3)
- religion (3)
- rendition (2)
- reports (1)
- Republican Party (3)
- Republicans (15)
- Richard Armitage (1)
- Richard Baker (1)
- Richard Clarke (1)
- Richard E. Stickler (1)
- Richard Mellon Scaife (2)
- Richard Nixon (2)
- Richard Perle (6)
- Richard Viguerie (1)
- Richard Wolffe (1)
- Rick Santorum (1)
- right-wing organizations (2)
- RNC (7)
- Robert Dreyfuss (1)
- Robert F. Kennedy Jr. (2)
- Robert Fisk (1)
- Robert Gates (9)
- Robert Johnson (1)
- Robert Kuttner (1)
- Robert Mueller (10)
- Robert Novak (3)
- Robert Parry (6)
- Robert Reich (1)
- Rodney Alexander (1)
- Roger Simon (2)
- Roger Stone (2)
- Romania (1)
- Ron Brownstein (2)
- Ron Paul (3)
- Ron Reagan (1)
- Ron Suskind (1)
- Ron Wyden (1)
- Ronald Reagan (3)
- Roslynn Mauskopf (1)
- Royal Dutch Shell (3)
- Royal Dutch/Shell Group of Cos. (1)
- Rudy Giuliani (5)
- Rudy Guiliani (1)
- rule of law (8)
- Rush Holt (1)
- Russ Feingold (2)
- Russell Feingold (1)
- Russell Simmons (1)
- Russia (4)
- Rwanda (1)
- Ryan Crocker (3)
- S. 1927 (4)
- S. 1932 (1)
- S. 2340 (1)
- S. Carolina (4)
- S. Dakota (1)
- S. Korea (1)
- Sabrina D. Harman (1)
- Saddam Hussein (3)
- Sadr City (1)
- SAIC (1)
- Sam Bodman (1)
- Sam Brownback (2)
- Samarra (2)
- San Francisco (4)
- sanctions (1)
- Sandra Day O'Connor (2)
- Sara Taylor (4)
- Sarah Palin (7)
- Sarkozy (1)
- Saudi Arabia (17)
- Savings and Loan crisis (3)
- science (2)
- Scooter Libby (8)
- Scott Ritter (2)
- SEC (1)
- secrecy (12)
- secret government (2)
- secret holds (1)
- secret prisons (4)
- Secret Service (3)
- secular democracy (1)
- Senate Appropriations subcommittee (2)
- Senate Armed Services Committee (3)
- Senate Energy and Commerce Committee (1)
- Senate Ethics Committee (1)
- Senate Finance Committee (2)
- Senate Intelligence Committee (6)
- Senate Judiciary Committee (22)
- Senate Republicans (1)
- senior issues (2)
- Separation of church and state (8)
- Sergeant Michael J. Smith (1)
- Sergeant Santos A. Cardona (1)
- sex (1)
- sex crimes (1)
- Seymour Hersh (7)
- Sheldon Adelson (2)
- Shell Oil (6)
- Sheryl Crow (1)
- Shiite militias (1)
- shrines (2)
- Sibel Edmonds (1)
- Sibiyha Prince (1)
- Sidney Blumenthal (2)
- SIGIR (1)
- signing statements (1)
- Slovakia (1)
- slow food (2)
- socialism (1)
- SOFA (1)
- Spain (2)
- Special Inspector General for Iraq Reconstruction (1)
- special ops (1)
- Specialist Charles Graner (1)
- speeches (2)
- Stephen Cambone (1)
- Stephen Hadley (8)
- Steve Capus (2)
- Steve Fraser (1)
- Steve McMahon (2)
- Steve Scalise (1)
- Steven Biskupic (1)
- Stuart Bowen (1)
- summer reading list (1)
- Sunni (2)
- sunshine laws (1)
- superdelegates (2)
- supplemental appropriations bill (9)
- Susan Collins (2)
- Susan Page (1)
- Susan Ralston (1)
- Swift Boat veterans (1)
- Swift Boat Veterans for Truth (1)
- Syria (13)
- T. Boone Pickens (1)
- Taguba report (2)
- Talabani (2)
- Taliban (2)
- TALON (1)
- TANG (1)
- taxes (1)
- Ted Kennedy (1)
- Ted Olson (1)
- Ted Stevens (2)
- Telecommunications Act (1)
- Telecoms (2)
- Tennessee (1)
- terrorism (12)
- Terrorist Surveillance Program (6)
- Terry McAuliffe (1)
- Terry O'Donnell (1)
- Texas (11)
- Thailand (1)
- The Fellowship (1)
- think tanks (3)
- Thom Hartmann (1)
- Thomas B. Edsall (1)
- Thomas Blanton (1)
- Thomas Edsall (1)
- Thomas J. Collamore (1)
- Thomas M. Tamm (1)
- Tim Geithner (7)
- Tim Griffin (1)
- Tim LaHaye (1)
- Tim Russert (2)
- Tim Ryan (1)
- Timothy P. Berry (1)
- Todd Graves (1)
- Todd Palin (3)
- Tom Allen (1)
- Tom Andrews (1)
- Tom Brokaw (1)
- Tom Coburn (1)
- Tom Coburt (1)
- Tom Daschle (1)
- Tom Davis (4)
- Tom DeLay (2)
- Tom Harkin (1)
- Tom Lantos (1)
- Tom Maertens (1)
- Tom Oliphant (1)
- Tom Tancredo (1)
- Tom Vilsack (1)
- Tommy Chong (1)
- Tony Blair (7)
- Tony Blankley (2)
- Tony Snow (2)
- tort reform (1)
- torture (51)
- Total (1)
- transcripts (47)
- trauma (2)
- Trent Lott (1)
- trial attorneys (1)
- TSA (1)
- Turkey (4)
- Tyler Drumheller (2)
- Tyumen Oil (1)
- U.S. Air Force (1)
- U.S. Army (2)
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (1)
- U.S. Army's Law of Land Warfare (1)
- U.S. Attorney Bill (1)
- U.S. Attorney General (8)
- U.S. Attorneys (23)
- U.S. bases (2)
- U.S. budget (1)
- U.S. Congress (16)
- U.S. Department of Agriculture (5)
- U.S. Department of Homeland Security (13)
- U.S. Department of Justice (3)
- U.S. Department of the Interior (1)
- U.S. Department of Transportation (1)
- U.S. District Court (1)
- U.S. dollar (4)
- U.S. Empire (1)
- U.S. foreign policy (18)
- U.S. House (10)
- U.S. military (62)
- U.S. Senate (13)
- U.S. State Department (6)
- U.S. Supreme Court (3)
- U.S. trade policies (5)
- U.S. Treasury Department (2)
- U.S.A. (1)
- U.S.S.C. (6)
- UAE (2)
- Ukraine (1)
- UN (7)
- UN Human Rights Commission (1)
- UN resolution 1483 (1)
- UN resolution 1546 (1)
- UN Security Council Resolution 687 (1)
- UNCC (1)
- UNICEF (1)
- unitary executive (2)
- Utah (2)
- Vaclav Klaus (1)
- Valerie Jarrett (1)
- Valerie Plame (12)
- Venezuela (2)
- Vermont (1)
- veterans affairs (1)
- VFW (1)
- Vicente Fox (1)
- video (26)
- video links (1)
- videos (21)
- Vince Cannistraro (1)
- Violence in America (1)
- Virginia (6)
- Vivian Stringer (1)
- voter caging (1)
- voter fraud (5)
- voter ID (3)
- Wal-Mart (1)
- Walter Reed Army Medical Center (1)
- war (2)
- war crimes (16)
- war czar (3)
- war in Afghanistan (24)
- war in Iran (19)
- war in Iraq (300)
- war in Vietnam (2)
- war on terror (51)
- war reparations (1)
- warrantless wiretaps (23)
- Warren Buffett (2)
- Washington (1)
- water (12)
- Watergate (1)
- Wayne LaPierre (1)
- wealth disparity (1)
- weapons (2)
- Wendy Cortez (1)
- Western Oilsands (1)
- Westinghouse (1)
- What The Hell Are They Thinking? (1)
- What's the matter with (4)
- Where are the Democrats? (3)
- whistleblowers (2)
- White House Office of Administration (1)
- White House Press Briefing (4)
- Who Broke America? (1)
- Why they hate us (11)
- William Arkin (1)
- William E. Colby (1)
- William J. Haynes (1)
- William Koch (1)
- William Kristol (2)
- William P. Weidner (1)
- William Pryor Jr. (1)
- Wisconsin (2)
- WMD (6)
- Wolf Blitzer (1)
- Wolfeboro (1)
- women (12)
- World Bank (3)
- worthless media (7)
- wounded veterans (2)
- WTO (1)
- Wyoming (1)
- Xe (2)
- Your tax dollars (2)
- YouTube (1)
- Zarqawi (2)
- Zogby (1)
- Zulfikar Ali Bhutto (1)
Elections 2008
Categories
[+/-] expand/collapse
- 10th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals (1)
- 1949 Geneva Conventions (3)
- 1949 Geneva Conventions-Fourth (1)
- 1949 Geneva Conventions-Third (1)
- 60 Minutes (1)
- 7th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals (1)
- 9/11/01 (12)
- Aaron Mate (1)
- Abdul-Mahdi (1)
- abortion (3)
- Abu Ghraib (13)
- ACLU (1)
- activism (1)
- Afghan civilians (1)
- Afghanistan (3)
- Ahmed Chalabi (1)
- Al Gore (1)
- Al Qaeda (3)
- Al Sharpton (2)
- al-Hashemi (2)
- al-Mahdi (1)
- al-Maliki (6)
- al-Sistani (1)
- Alaska (5)
- Alberto Gonzales (13)
- alternative media (1)
- American culture (13)
- Amy Goodman (1)
- An Inconvenient Truth (1)
- Analysis Corp (1)
- Andrew Card (3)
- animals (3)
- Anthony Zinni (1)
- anthrax (1)
- antiquities (1)
- Antonia Juhasz (2)
- Arent Fox Kintner Plotkin and Kahn (1)
- Arizona (1)
- Arlen Specter (2)
- Armstrong Williams (3)
- asbestos (2)
- Atlanta (1)
- Barack Obama (3)
- Barbara Bush (2)
- BCCI (1)
- Bearing Point (1)
- bees (2)
- benchmarks (2)
- Benita Fitzgerald Mosley (2)
- Big Agra (1)
- Big Oil (2)
- Big Pharma (1)
- Bill Clinton (1)
- Bill Kristol (1)
- Bill Maher (1)
- Blackstone (1)
- blogging (2)
- Bob Shrum (1)
- Bolivia (1)
- books (9)
- boys will be boys (1)
- BP (3)
- BP America (1)
- BP PLC (1)
- Bradley Schlozman (1)
- Bremer's 100 Orders (2)
- Brian Schweitzer (1)
- Brigadier General Janis Karpinski (2)
- Bruce Bartlett (1)
- Bud Cummins (1)
- Bush (14)
- Bush administration (10)
- Bush's surge (4)
- CAFTA (1)
- Canada (1)
- cancer (1)
- capitalism (2)
- Carlyle Group (3)
- Caroline Cheeks Kilpatrick (1)
- CBS (3)
- censorship (3)
- Chad (1)
- Chalmers Johnson (1)
- Charles Koch (2)
- Charlie Rangel (1)
- Chevron (2)
- ChevronTexaco (1)
- children (1)
- China (4)
- Chip Reid (1)
- Chris Dodd (2)
- Chris Matthews (4)
- Chris Van Hollen (1)
- Christopher Hitchens (1)
- Chuck Schumer (2)
- CIA (11)
- Clarence Page (2)
- climate change (1)
- Clinton administration (1)
- coal (1)
- Coalition Provisional Authority (4)
- Colleen Rowley (2)
- Colonel Thomas M. Pappas (3)
- Connecticut (1)
- Conoco (1)
- ConocoPhillips (1)
- Conservatives (1)
- conspicuous consumption (1)
- contractors (3)
- corruption (6)
- CPA (9)
- Craig Crawford (2)
- Cuba (11)
- culture (5)
- Cynthia Tucker (1)
- Cyril Wecht (1)
- D and E/D and X/Partial Birth Abortion (2)
- Dan Burton (1)
- Dan Rather (1)
- David Gergen (1)
- David Gregory (6)
- David Horgan (1)
- David Koch (2)
- David MacMichael (1)
- David Shuster (1)
- death toll (1)
- debates (2)
- Defense Policy Board (1)
- Deforest Soaries (3)
- Democracy Now (1)
- Democrats (3)
- deregulation (1)
- Det Norske Oljeselskap (1)
- Dianne Feinstein (1)
- Dick Cheney (7)
- Dick Cheney's energy task force (3)
- dissent (1)
- Diyala (1)
- DNO (2)
- DOJ (1)
- domestic spying (1)
- Don Evans (1)
- Don Imus (6)
- Donald Rumsfeld (7)
- Douglas Brinkley (1)
- Douglas Feith (1)
- drug bill (1)
- drugs-illicit (2)
- Duncan Hunter (1)
- Ebay (1)
- economy (6)
- Egypt (1)
- election 2008 (3)
- election reform (2)
- election 2006 (1)
- elections 2008 (13)
- Elian Gonzalez (1)
- Elijah Cummings (1)
- email (1)
- energy (9)
- energy policy (3)
- entertainment (3)
- environment (13)
- EPA (1)
- Eugene Robinson (2)
- ExxonMobil (4)
- Faye Williams (1)
- FBI (4)
- FDA (2)
- Federalist Society (1)
- financial disclosure (1)
- first amendment (1)
- flat tax (1)
- food (8)
- Frank Murkowski (1)
- Fred Koch (1)
- Fred Thompson (11)
- freedom and democracy in Iraq (2)
- Futile Care Law (1)
- Gazprom (1)
- gender inequality (1)
- Genel Enerji (1)
- General David Petraeus (1)
- General Electric (1)
- George H.W. Bush (2)
- George Tenet (12)
- Georgia Pacific Corp. (1)
- Georgia Thompson (1)
- Getting to Know Your Adversary (1)
- global warming (4)
- GMO (1)
- Gonzales vs. Carhart (1)
- Governor Jim Doyle (1)
- Great Britain (2)
- Grover Norquist (1)
- Guantanamo (10)
- Gulf of Mexico (1)
- General David Petraeus (1)
- Guatemala (1)
- guns (1)
- H.R. 1591 (1)
- Hague Regulations of 1907 (3)
- Halliburton (2)
- Hardball (9)
- Harry Reid (2)
- Hawaii (1)
- health (16)
- health insurance (1)
- Helms-Burton Act (1)
- Henry Paulson (1)
- Hillary Clinton (3)
- homeland security (1)
- House Committee on Intelligence (1)
- House Judiciary Committee (1)
- Howard Fineman (2)
- Hugo Chavez (1)
- human rights (10)
- illegal immigration (2)
- IMF (3)
- implosions (10)
- In our names (1)
- intelligence (1)
- Internet (5)
- interviews (4)
- IPO (1)
- Iran (2)
- Iraq (28)
- Iraq czar (1)
- Iraq elections (2)
- Iraq Health Ministry (1)
- Iraq reconstruction (5)
- Iraq Study Group (1)
- Iraqi civilians (12)
- Iraqi Islamic Party (1)
- Islam (1)
- Issam al-Chalabi (1)
- Iyad Allawi (1)
- James Yousef Yee (1)
- James Baker (2)
- James Comey (5)
- Jane Harman (1)
- Jean-Baptiste Aristide (1)
- Jean-Bertrand Aristide (1)
- Jesse Helms (1)
- Jim Marcinkowski (1)
- Jim Miklaszewski (1)
- Jim VandeHei (1)
- Jimmy Carter (1)
- Joan Baez (1)
- Joe Lieberman (1)
- John Ashcroft (6)
- John B. Taylor (1)
- John Boehner (1)
- John Edwards (1)
- John Harris (2)
- John Kerry (1)
- John McCain (3)
- John Mellencamp (1)
- John Murtha (1)
- Joint Chiefs of Staff (1)
- Jonathan Alter (1)
- Jordan (1)
- K Street (2)
- Kamil Mubdir Gailani (1)
- Karl Rove (7)
- Kate O'Beirne (1)
- Ken Blackwell (1)
- King Abdullah (1)
- Kit Bond (1)
- Koch brothers (2)
- Koch Industries (1)
- KRG (1)
- Kurdistan (2)
- Kurdistan Regional Government (1)
- Kurds (5)
- Kyle Sampson (1)
- L-1 Identity Solutions (1)
- Lancet Study (9)
- Larry Johnson (1)
- Las Vegas (3)
- Laurie David (1)
- Lee Hamilton (1)
- legislation (1)
- Lieutenant General Ricardo S. Sanchez (1)
- Lisa Murkowski (1)
- lobbyists (2)
- Lois Romano (1)
- Lt. Colonel Steven Jordan (1)
- Lt. General Douglas Lute (2)
- Lukoil (1)
- Lynndie England (1)
- Mahmoom Khaghani (1)
- Maine (1)
- Major General Antonio Taguba (1)
- Major General Benjamin R. Mixon (1)
- Major General Geoffrey Miller (11)
- Mark Corallo (1)
- Mark Pryor (1)
- Mary Beth Buchanan (1)
- Maryland (1)
- Maury Wills (1)
- media (3)
- medical ethics (1)
- Meet the Press (1)
- mental health (3)
- mental illness (1)
- Mexico (1)
- Michael Eric Dyson (1)
- Michael Moore (4)
- Michael Scheuer (1)
- Mickey Herskowitz (1)
- Middle East (2)
- Mike Barnicle (1)
- Mike Huckabee (1)
- military equipment (1)
- Mitt Romney (4)
- Monica Goodling (1)
- Montana (1)
- MSNBC (3)
- NAFTA (1)
- Nancy Pelosi (1)
- Naomi Klein (8)
- National Security (1)
- Nelson Cohen (3)
- New Hampshire (1)
- New Iraq (12)
- New World Order (2)
- New York (1)
- NIY (1)
- nuclear (1)
- oil and gas (19)
- oil law (15)
- OPEC (1)
- Operation Rescue (1)
- Order 37 (2)
- Order 39 (3)
- Order 40 (1)
- organized labor (1)
- Orrin Hatch (1)
- Pat Buchanan (2)
- Pat Leahy (1)
- Patrick McHenry (1)
- Patriot Act (4)
- Patty Murray (1)
- Paul Bremer (8)
- Paul Eaton (1)
- Paul O'Neill (1)
- Paul Rieckhoff (1)
- Paul Wolfowitz (2)
- PDVSA (1)
- General David Petraeus (1)
- Pentagon (2)
- Pete Domenici (1)
- Petoil (1)
- Petrel Resources (1)
- Phil Gingrey (1)
- Phil Giraldi (1)
- Phil Griffin (1)
- Phillipines (1)
- photos (1)
- Plan B (1)
- Presidential candidates (1)
- privacy (4)
- private equity (1)
- privatization (4)
- Profiles (12)
- propaganda (4)
- PSA (1)
- Putin (1)
- QinetiQ (1)
- Ray McGovern (1)
- Reasons not to vote for Republicans (3)
- Reasons we need campaign finance reform (1)
- refugees (1)
- religion (1)
- rendition (1)
- Republicans (3)
- Richard Clarke (1)
- Richard Nixon (1)
- Richard Perle (4)
- Bill Richardson (1)
- Reasons we need campaign finance reform (1)
- Robert Johnson (1)
- Robert Kuttner (1)
- Robert Mueller (5)
- Roger Simon (2)
- Ron Paul (1)
- Ron Reagan (1)
- Ron Suskind (1)
- Ronald Reagan (2)
- Royal Dutch/Shell Group of Cos. (1)
- Rudy Giuliani (3)
- Rush Holt (1)
- Russ Feingold (1)
- Russell Simmons (1)
- Ryan Crocker (1)
- Sabrina D. Harman (1)
- Saddam Hussein (1)
- SAIC (1)
- Sam Bodman (1)
- Saudi Arabia (2)
- Reasons we need campaign finance reform (1)
- secular democracy (1)
- Senate Energy and Commerce Committee (1)
- Senate Judiciary Committee (6)
- Sergeant Michael J. Smith (1)
- Sergeant Santos A. Cardona (1)
- Shell Oil (4)
- Sheryl Crow (1)
- Shiite militias (1)
- Sibiyha Prince (1)
- SIGIR (1)
- socialism (1)
- Special Inspector General for Iraq Reconstruction (1)
- Specialist Charles Graner (1)
- speeches (1)
- Specialist Charles Graner (1)
- Stephen Cambone (2) Stephen Hadley (3)
- Steve Capus (2)
- Steve McMahon (2)
- Steven Biskupic (1)
- Stuart Bowen (1)
- Sunni (1)
- supplemental appropriations bill (1)
- Susan Collins (1)
- Syria (1)
- Taguba report (1)
- Talabani (2)
- TALON (1)
- TANG (1)
- Ted Olson (1)
- Ted Stevens (2)
- terrorism (1)
- Terrorist Surveillance Program (1)
- Texas (3)
- think tanks (2)
- Tim Griffin (1)
- Tim Russert (1)
- Todd Graves (2)
- Tom Allen (1)
- Tom Brokaw (2)
- Tom Oliphant (1)
- Tom Tancredo (2)
- Tommy Chong (1)
- Tony Blair (2)
- Tony Blankley (2)
- Tony Snow (2)
- torture (15)
- transcripts (12)
- Turkey (3)
- U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (1)
- U.S. Army's Law of Land Warfare (2)
- U.S. Attorneys (11)
- U.S. bases (1)
- U.S. Congress (1)
- U.S. Department of Homeland Security (1)
- U.S. Department of the Interior (1)
- U.S. dollar (1)
- U.S. Empire (1)
- U.S. foreign policy (9)
- U.S. military (18)
- U.S. Senate (3)
- U.S. Supreme Court (2)
- U.S. trade policies (1)
- U.S. Treasury Department (2)
- UN (3)
- UN resolution 1483 (1)
- UN resolution 1546 (2)
- Venezuela (1)
- VFW (1)
- video (16)
- video links (1)
- Vince Cannistraro (1)
- Violence in America (1)
- Virginia (1)
- Vivian Stringer (1)
- voter fraud (5)
- voter ID (3)
- Wal-Mart (1)
- Walter Reed Army Medical Center (1)
- war crimes (3)
- war czar (2)
- war in Afghanistan (9)
- war in Iraq (99)
- war on terror (6)
- warrantless wiretaps (4)
- Western Oilsands (1)
- Westinghouse (1)
- Where are the Democrats? (1)
- whistleblowers (1)
- White House press briefing (2)
- William Arkin (1)
- William Koch (1)
- Wisconsin (2)
- WMD (1)
- Wolfeboro (1)
- women (2)
- World Bank (1)
- YouTube (1)
Congressional Bios & Voting Records
Blog Archive
-
▼
2007
(817)
-
▼
April
(72)
- Torn Between Democracy, The Military and Islam
- The Greatest Threat To Humankind - Animal Extincti...
- Transcript of Hardball with Chris Matthews, April ...
- Major Problems Found In Iraqi Rebuilding Effort
- Why There Is No Exit Plan
- The Proposed Iraqi Oil Law
- Transcript of George Tenet on 60 Minutes - April 2...
- Egypt To Propose Iraq Cease-Fire At Conference; Ba...
- Foreign Oil Projects Stall In Wait For Iraqi Permits
- Kurds to Block Iraq Oil Law
- Stephen Hadley: Looking For Mr. War Czar
- Iranian Envoy Tells Iraq's Al-Maliki: "U.S. Milita...
- Bill Kristol Defends Co-PNAC-Signator, Richard Per...
- What The Chinese Are Putting In Our Food
- Michael Scheuer's Op-Ed on George Tenet's Book & 6...
- An Open Letter To George Tenet
- Time's Interview with George Tenet
- The Excerpted George Tenet
- Maliki's Office Is Seen Behind Purge In Forces
- The Afghan Beauty School
- Bush's Interior Department To Announce Plans To Dr...
- Vitamin D Casts Cancer Prevention in New Light
- The Selling Off Of America's Infrastructure
- Dollar's Drop Challenges U.S. Power
- CIA Transfers Senior Al Qaeda Leader To Guantanamo
- Alaska's U.S. Atty Nelson Cohen, A Patriot Act App...
- South Carolina Democratic Debate - 4/26/07
- Pentagon Urged To Close Secret Database
- What Role For Democratic 'Super-Delegates'?
- From The White House To Abu Ghraib
- UN Raps Iraq for Withholding 'Grim' Civilian Toll
- Who Decides?
- Giuliani On The Primary Trail: "Only Republicans C...
- Fascist America, in 10 Easy Steps
- What's Happening To The Bees?
- From The CourtHouse To The White House
- The Adhamiyah Wall
- Profile: Ryan Crocker, U.S. Ambassador To Iraq
- Alaska's U.S. Attorney Nelson Cohen - Another Patr...
- Alaska Fails To Sell State Jet On Ebay
- U.S. Scandal Threatens Alaska's Prosecutor
- Karl Rove, Laurie David, Sheryl Crow, White House ...
- You Are What You Grow
- Colleges Face Surge of Troubled Students
- Giuliani Shifts Stance On Abortion Method
- Anti-abortion activists look to build on court vic...
- Virginia Tech Shooter's History Raised Red Flags W...
- Demand For Wood Flooring Is Destroying Endangered ...
- At The Heart Of The U.S. Attorneys' Flap
- Can Bush Prevent Non-Disruptive Dissenters From Ta...
- Heroes and Villains
- TCA Book Bin: "Oil on the Brain," by Lisa Margonelli
- Desecration Of The Cradle Of Civilization
- U.S. Military Sharpens Focus On Climate Change
- Three Times A Charm?
- Documents Show DOJ Considered Political Credential...
- Turkish Army Demands Incursion Into Iraq
- On Hardball with Chris Matthews, April 13, 2007
- Payouts Reveal Iraq Civilian Toll
- Battling Over The World's Oil Reserves
- On Hardball with Chris Matthews, April 12, 2007
- On Hardball with Chris Matthews, April 11, 2007 - ...
- 500 Terror Attacks in EU in 2006 . . . .
- Fred Thompson Has Lymphoma
- On Hardball with Chris Matthews, April 11, 2007 - ...
- On Hardball with Chris Matthews, April 10, 2007
- On Hardball with Chris Matthews, April 9, 2007
- Foreign Policy: "Iraq Study Group Has Set U.S. Pol...
- Boys Contaminate W.Virginia Town With Mercury
- Is Hillary Secret Rev. Al Ally?
- Fred Thompson, Capitol Hill Lobbyist
- On Meet The Press - April 1, 2007
-
▼
April
(72)